CSR: Samudra Manthan Initiative Conducted for Dadar Beach Clean up 2024
Mumbai’s leading real estate developer Sugee Group, in collaboration with Jay Foundation, which works for preservation of environment by undertaking beach cleaning and other environment betterment initiatives every year, organised a beach clean-up programme – ‘Samudra Manthan’ – at Mumbai’s Dadar Beach.
‘Samudra Manthan’ Dadar Beach Clean-up Drive initiative witnessed participation from all the nature loving youths, students and diverse participants from all across Dadar and other parts of Mumbai. As a community initiative, the employees and associates of Sugee Group also actively participated in this beach-side environment clean – up drive.
Sugee Group has been supporting Jay Foundation in organising this beach clean – up programmes for the past few years. Promoted by an ocean lover and environmentalist, Mr Jay Shringarpure, Jay Foundation conducts various orientation programmes for the youth and teenagers to create awareness about the importance of ocean cleaning and educate them on various aspects of sustainability and sustainable living.
Commenting on its unwavering support to this initiative, Mr Nishant Deshmukh, Founder and Managing Director “We are once again happy to be a part of Dadar Beach Clean – Up initiative ‘Samudra Manthan’. This drive, true to its name, effectively cleared the beach of garbage and plastic waste. As a leading real estate developer, we strongly advocate for a clean and green environment in the vicinity, crucial for sustainable living. Every element of urban infrastructure including the oceans and water bodies need to be well protected from an environmental perspective. We proudly support this community building initiative by Jay Foundation Jay Foundation, which is engaging in creating social awareness about preserving the ecologies of our beaches and fostering a sense of communal responsibility.”
Talking about his concerted efforts to save beaches through beach clean – up activities, Mr Jay Shringarpure said, “This is the seventh successful year of our beach clean – up drive and every year the participation from environment – conscious citizens is just increasing, which is a good sign. The oceans and beaches are irreplaceable and hence, we must save them. We are happy to have environment – sensitive partners like Sugee Developers, which has strengthened our resolve to protect the environment.”
Adding further, he said, “Samudra Manthan” Beach clean – ups are important to mitigate the problem caused by ocean debris and the danger that plastic pollution poses to marine life. We want to inculcate the sense of responsibility amongst youngsters, who are the future of tomorrow and for whom this coastal environment needs to be well-preserved.”
Till date, more than 1,000,00 volunteers have participated in this campaign and helped remove more than 9,000 tonnes of plastic and other garbage from over 450 beaches.
On 11th December, 2021, Jay Foundation Jay Foundation in support from Sugee Group created a history by undertaking the biggest beach cleaning campaign that was recognised by the Limca Book of Records. Jay Foundation Jay Foundation has been undertaking campaigns and initiatives like beach clean-ups, plastic collection, green smiles – a walk for oceans, etc.
Disclaimer: This media release is auto-generated. The CSR Journal is not responsible for the content.
Empowering Women Athletes through CSR Partnership
In line with its commitment to sports, Coca-Cola India through its Foundation, is supporting the country’s athletes with essential amenities and training equipment as part of its three-year partnership with the Anju Bobby Sports Foundation. Spearheaded by Olympic champion Anju Bobby George, the Foundation has been nurturing the next generation of women athletes including the very known long jumper- Shaili Singh. This partnership aligns with Coca-Cola India’s #SheTheDifference campaign, an initiative to celebrate, uplift, and support women throughout the value chain. As part of this partnership, Coca-Cola India is committed to empowering women athletes to bring about positive change in the sports and gender equality landscape.
Coca-Cola India, through its Foundation, has made significant strides in bolstering the representation of Indian women athletes in the Olympics. The company has transformed four shipping containers into a physiotherapy room, storage facility, pantry, and restroom. The company also facilitated top-tier gym equipment and supported the establishment of a spacious practice ground equipped with rainwater collection tanks for sustainable water usage. In addition to infrastructure development, Coca-Cola has helped with the academy’s lease rent for three years, ensuring a stable operational foundation.
In a nation where many female athletes emerge from small towns and villages, facing limited access to training facilities, coaching, and financial support, this collaboration aims to level the playing field. A PWC report highlights the remarkable shift in the gender balance at the Tokyo Olympics, with 44% of Indian participants being women.
Commenting on the partnership, Rajesh Ayapilla, Director-CSR and Sustainability for Coca-Cola India and Southwest Asia (INSWA), said, “At Coca-Cola India, we believe in the power of sports to inspire, empower, and unite communities. Our longstanding partnership with the Anju Bobby Sports Foundation reflects our commitment to fostering the next generation of Indian women athletes. With sports being an integral part of both organizations’ DNA, through such initiatives, we are dedicated to creating a supportive environment where athletes can thrive. We are proud to sponsor talented individuals like Shaili Singh, reaffirming our commitment to empowering women in sports and contributing to their success on the global stage”.
“I feel honored to be associated with such a brand like Coca-Cola India. They were the first ones to support our cause and their contribution has been instrumental in creating a world-class training facility in India at the Anju Bobby High Performance Center, Bangalore. Today, we have some top-quality track and field equipment, some of the quality gym equipment, and our athletes here are focused on making the most of these facilities to help India win its Olympic medal. Personally, as well, I feel if I could win India’s first world championship medal, it’s my duty to share my knowledge and experience with these young women, thereby contributing to India’s success”, said Anju Bobby George, Founder, Anju Bobby Sports Foundation.
The social impact of this initiative extends beyond individual achievements in the field. By empowering women athletes, the Foundation along with Coca-Cola India is nurturing future leaders who will contribute back to the sports community as coaches, trainers, therapists, and administrators.
Disclaimer: This media release is auto-generated. The CSR Journal is not responsible for the content.
Election Report Card: Promises Vs Achievements in Foreign Policy of India
Election is a very important tool in democracy. It is through election that citizens of a nation choose their representatives and select their leaders. Political leaders represent different political parties which work for various goals.
In the general election held in 2014, the BJP-led NDA secured 282 seats and formed the government, making Narendra Modi the Prime Minister of India, while in the 2019 elections the number of seats went up to 303. The much-awaited Lok Sabha Elections 2024 will commence from 19th April, for which Prime Minister Narendra Modi has set a target of 370 seats for the ruling BJP and 400 seats for the NDA.
With the Lok Sabha Elections 2024 a few days away, how to decide which political party you should cast your vote for? How to know how much work the party in power has done as against the tall claims that were made right before the previous elections?
The CSR Journal, which is known for its unbiased and fearless journalism delves into promises made versus task completed by the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP), which is incumbent at the Centre under the leadership of Prime Minister Narendra Modi.
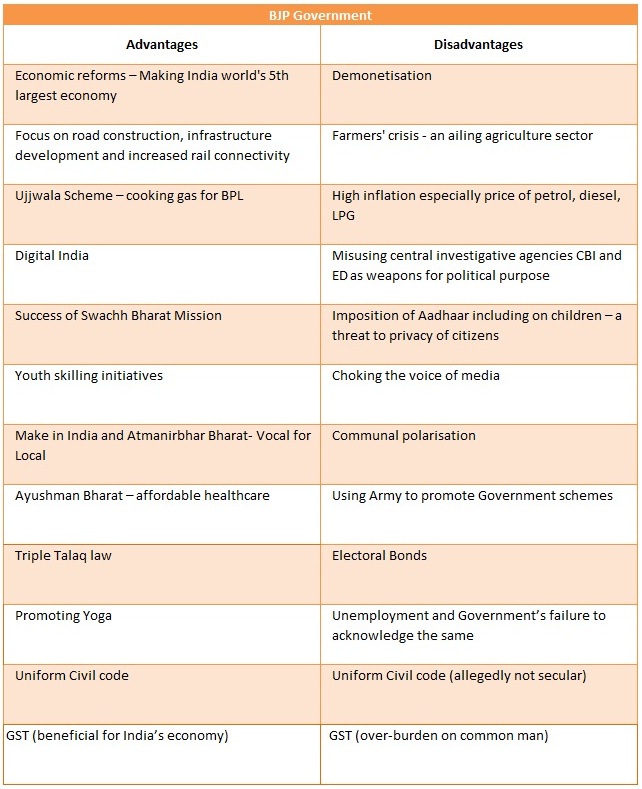
Following are certain promises made under the BJP’s manifesto ahead of the Lok Sabha Elections 2019. How much of the promises have been achieved in the past 5 years? Were the decisions made by the government beneficial for its people? Are citizens happy with what the government has to offer? The CSR Journal takes a look.
BJP Manifesto – Lok Sabha 2019
Promises made by the Narendra Modi Government for: Foreign Policy
1. Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam
2. Global Coordination on Knowledge and technology
3. Continuous Dialogue with Indians Living Abroad
4. Combating Terrorism through Global Forums
5. Deeper Multilateral Cooperation
6. Permanent Membership of the United Nations Security Council
7. Strengthening the Diplomatic Cadre and Outreach
‘Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam’
Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam is a Sanskrit phrase that means “The World is One Family.” This ancient Indian philosophy promotes the idea of shared humanity and peaceful coexistence among all peoples and nations. It emphasizes values like compassion, cooperation, and interdependence on a global scale. In recent decades, Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam has become an important guiding principle shaping India’s foreign policy outlook and approach to international relations.
India has actively worked to promote the spirit of Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam through initiatives like the International Solar Alliance co-founded with France, and forums like the Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA) and Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC). It has advocated for peaceful dialogue and diplomatic solutions, exemplified by its support for the Iran nuclear deal and role in the Afghanistan peace process. India has also positioned itself as a voice for developing nations through platforms like the BRICS and its calls for UN reforms.
Furthermore, India has leveraged the philosophy to broaden economic and cultural cooperation through free trade agreements with countries like Mauritius and South Korea, and ambitious connectivity initiatives like the Kaladan Multi-Modal Transit Transport Project with Myanmar. The economic initiatives like the International Solar Alliance position India as a catalyst for collective action on sustainable development and climate change impacting the entire global family.

Upholding Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam has been a core principle guiding India’s ongoing G20 Presidency in 2023 under the theme of “Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam: One Earth, One Family, One Future.” Major outcomes have included the launch of the Human Life Value Transformation (HLVT) movement and concrete commitments on issues like debt restructuring, crypto regulations and mobilizing climate finance. At its essence, this philosophy represents India’s commitment to a multi-polar world order based on equality, mutual respect and international cooperation as it cements its role as a leading power and voice for the global south.
However, the ability to fully operationalize this philosophy on a global scale has faced challenges. For example,
Differences persisted among G20 members on issues like the Russia-Ukraine conflict.
Concerns around protectionism, unilateral policies impacted cooperation on trade and economics.
Global solidarity remained inadequate in areas like pandemic prevention and climate action.
So while India sincerely tried to promote Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam ideals as G20 President, the reality of geopolitical tensions and national interests posed obstacles in fully realizing the “One Family” vision across all G20 outcomes and processes.
Ultimately, upholding values like Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam is an ongoing endeavor requiring consistent diplomacy and global cooperation over the long-term. India’s G20 Presidency helped renew focus on this unifying philosophy, even if practical implementation remains an uphill battle.
Global Coordination on Knowledge and Technology
India embarked on several initiatives aimed at bolstering international cooperation in the realms of science, technology, and innovation. In 2019, the Global Innovation Partnership (GIP) was introduced, fostering collaborative innovation endeavors between Indian and foreign universities and research institutions. This initiative aimed to harness the collective expertise and resources of diverse stakeholders to address global challenges and drive technological advancements. By facilitating joint projects and knowledge exchange, the GIP sought to accelerate progress in key areas such as healthcare, renewable energy, and information technology.
The following year, in 2020, India assumed the role of a founding member in the Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence (GPAI), aimed at formulating responsible AI standards. With the rapid proliferation of AI technologies across various sectors, India recognized the importance of shaping ethical frameworks and guidelines to ensure their safe and beneficial deployment. As a member of GPAI, India collaborated with other nations to develop principles that promote transparency, accountability, and inclusivity in AI development and deployment. Through this partnership, India aimed to contribute to the responsible adoption of AI technologies on a global scale, fostering trust and confidence in their use.
Additionally, in 2021, the Vaccine Action Program (VAP) was initiated, serving as a hub for technology transfer to facilitate global vaccine production. Recognizing the critical role of vaccines in combating infectious diseases and promoting public health, India launched this program to share its expertise in vaccine development and manufacturing with the international community. By establishing technology transfer hubs and fostering collaboration with pharmaceutical companies and research institutions worldwide, India aimed to expand access to affordable and high-quality vaccines, particularly in low- and middle-income countries.
Various agreements were also inked with partner nations such as the UK, Israel, and Brazil to establish joint centers and funds, fostering research collaboration. These partnerships aimed to leverage complementary strengths and expertise to address shared challenges and pursue common research objectives. By pooling resources and expertise, India and its partners aimed to accelerate scientific discovery, innovation, and technological development in key priority areas.
Despite these endeavors, the realized progress and tangible outcomes appeared modest compared to the initial ambitions. The pandemic-induced years witnessed reduced mobility for students and researchers, constraining academic exchanges. Funding challenges posed hurdles affecting the scale and scope of initiatives like GIP and VAP. Notably, advancements on major connectivity and data-sharing platforms, crucial for seamless knowledge dissemination, were lacking. India’s engagements in global technology domains remained predominantly bilateral rather than driving novel plurilateral frameworks.
While these steps were well-intentioned, the Indian government achieved only partial success in catalyzing an era of heightened global coordination in knowledge and technology arenas during this period. The disruptions caused by COVID-19 and resource constraints likely curtailed the ability to fully realize the promises made in 2019. Nevertheless, the initiatives launched during these years could serve as foundational elements for more robust international partnerships in science and innovation in the years ahead. Renewed dedication and focus would be imperative to actualize India’s objectives in this domain going forward.
Continuous Dialogue with Indians Living Abroad
The Indian diaspora, estimated at over 30 million people across the world, has been an important focus area for successive Indian governments. In the latest term of Government of India under the leadership of Prime Minister Narendra Modi, took following initiatives for the benefit of Indians living abroad:

Regular annual Pravasi Bharatiya Divas conventions served as significant diaspora outreach programs, even transitioning to virtual formats during the pandemic years to ensure continuity. Additionally, regional Pravasi Bharatiya Divas events were organized in countries such as Singapore, the UK, and Canada, facilitating connections with diaspora communities abroad. The expansion of the “Study in India” program aimed to attract more diaspora students to Indian universities, enhancing educational opportunities and cultural exchange.
Reforms were also implemented in schemes like the Overseas Citizen of India (OCI) and Global Pravasi Rishta to address longstanding grievances within the diaspora community. The operationalization of the MADAD online grievance redressal portal provided a platform for consular assistance and feedback from diaspora members.
However, certain challenges persisted. COVID-19 travel restrictions hindered physical outreach efforts for a period, limiting direct engagement with diaspora populations. Concerns regarding the welfare of Indian migrant workers in certain regions remained prevalent, highlighting ongoing issues that required attention.
Furthermore, some diaspora groups expressed concerns about domestic policies impacting their cultural and religious identities, necessitating dialogue and understanding between the government and diaspora representatives. Capacity building within the government’s diaspora engagement infrastructure was identified as an area needing improvement. While the Indian government demonstrated commitment through frequent high-level interactions and policy measures, maintaining seamless two-way communication with diaspora communities worldwide remained a work in progress until August 2023. Continued dedicated efforts would be necessary to fully realize the potential of diaspora engagement and address the diverse needs and concerns of the global Indian community.
Combating Terrorism through Global Forum
India demonstrated unwavering commitment to rallying global cooperation against the menace of terrorism across multilateral platforms.
At the United Nations, India championed the early finalization of a Comprehensive Convention on International Terrorism. Its Permanent Representative Ruchira Kamboj affirmed, “We remain committed to bringing those responsible for perpetrating these inhuman acts to justice.”

External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar, without naming Pakistan or China, criticized countries that use terror as a “tool of state-craft” or fail to “rise above political divides” to address the threat posed by terrorism. He emphasized that perpetrators, facilitators, and financiers of terror attacks “continue to walk free, enjoy state support and hospitality,” citing the “most egregious example” of the 2008 Mumbai terror attack. Jaishankar called for concerted action against terrorists and their sponsors, including dismantling safe havens and political support structures.
Recognizing terrorism as a “grave threat to humanity itself,” India leveraged regional forums like BRICS, SAARC and SCO to build counterterrorism capacities and intelligence-sharing mechanisms. Strong counterterrorism partnerships were forged with nations like the U.S., Russia and European countries.
While challenges persisted, India’s voice reverberated globally on the need for a unified zero-tolerance approach.

In 2023, India marked a significant milestone in its relentless pursuit of safety, security, inclusivity, and self-reliance under the visionary leadership of Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi. The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) witnessed a paradigm shift in the criminal justice system with the passage of landmark legislations including the Bharatiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita, Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita, and Bharatiya Sakshya Adhiniyam, ushering in a new era of legal frameworks aligned with contemporary needs and correctional ideologies. Upholding a zero-tolerance policy against terrorism and drug trafficking, India, under the decisive guidance of Home Minister Shri Amit Shah, declared four organizations as ‘Terrorist Organizations,’ designated seven individuals as ‘Terrorists,’ and identified three organizations as ‘Unlawful Associations.’ This proactive stance reinforced India’s commitment to combating the global scourge of terrorism.
Furthermore, significant strides were made towards promoting peace, progress, and development in conflict-prone regions such as Jammu & Kashmir, the North East, and Left Wing Extremism (LWE) areas. Historic agreements were signed to settle long-standing disputes and foster reconciliation, including the resolution of the border dispute between Assam and Arunachal Pradesh and the signing of a Peace Agreement with the United National Liberation Front (UNLF) in Manipur. These initiatives were pivotal in realizing Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi’s vision of a peaceful, prosperous, and insurgency-free Northeast.
Moreover, efforts were intensified to bolster national security and strengthen border infrastructure, with the establishment of security camps in Maoist strongholds and the initiation of the Vibrant Villages Programme aimed at comprehensive development of border villages. In alignment with contemporary needs, the MHA embarked on a comprehensive review and revision of outdated colonial-era laws, underscoring its commitment to modernizing the legal framework.
As India navigated the challenges of the digital age, initiatives were launched to curb cybercrimes and enhance disaster management capabilities. The introduction of millets (Shree Anna) in the meals of Central Armed Police Forces (CAPFs) and National Disaster Response Force (NDRF) personnel underscored India’s commitment to promoting healthy and sustainable dietary practices.
Deeper Multilateral Co-operation
India, a nation with a rich history and diverse cultural heritage, has consistently played a pivotal role in global affairs. As part of its foreign policy, India recognizes the significance of deeper multilateral co-operation. This strategic approach aims to foster collaboration, enhance regional stability, and address global challenges.

Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s foreign policy doctrine emphasizes strategic autonomy and active global engagement. In his words, “A strong, self-reliant, and self-confident India will pursue a foreign policy of enlightened self-interest.” This doctrine underscores India’s commitment to multilateralism while safeguarding its national interests.
India actively engages in several key multilateral partnerships, collaborating with nations and organizations to address global challenges. Let’s explore some of these significant partnerships:
BRICS (Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa)
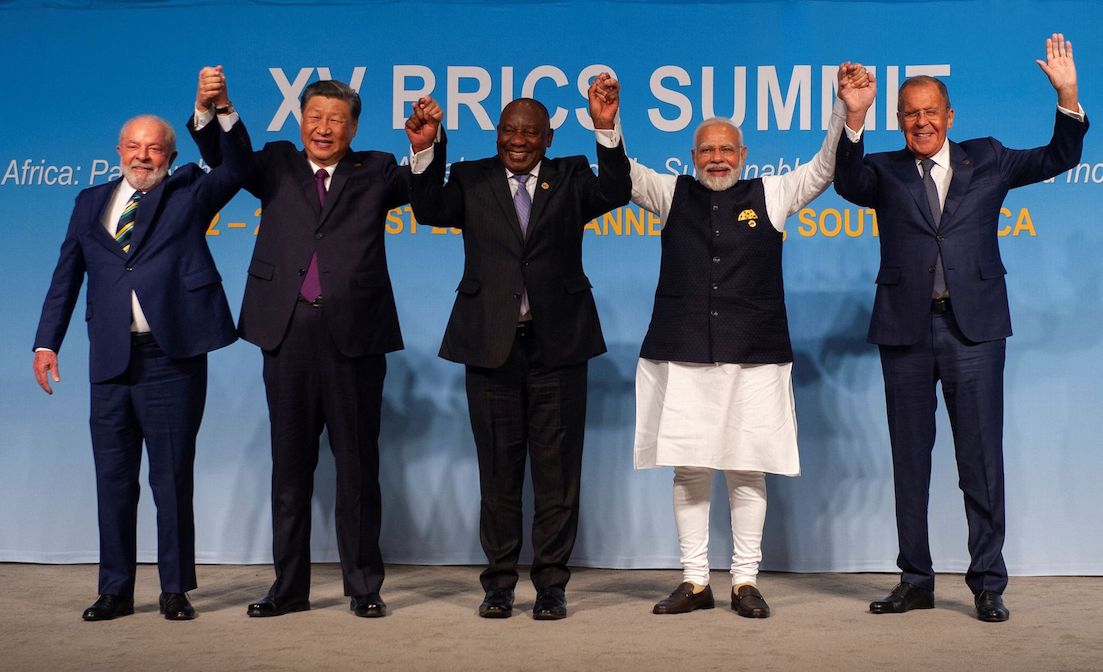

BRICS, originally comprising Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa, has now expanded its membership from five to eleven countries. This move reflects a concerted effort to enhance its global standing. Egypt, Iran, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Ethiopia, and Argentina have joined the BRICS fold, amplifying the group’s representation across the Middle East, Africa, and South America. Full membership for these new entrants will take effect on January 1, 2024. While the original BRIC members shared large economies and high growth rates, the expanded BRICS-11 is a more diverse group, with some countries facing crises and others thriving. This expansion could signal a broader agenda beyond economics.
G20 (Group of Twenty)

As a member of the G20, India participates in discussions on global economic governance, financial stability, and development. The G20 provides a platform for India to engage with major economies and address pressing issues.
In December 2022, Prime Minister Narendra Modi assumed the G20 presidency, receiving the gavel from his Indonesian counterpart in Bali. India’s presidency provides an opportunity to shape the global agenda and promote its priorities.
In 2023, India hosted the G20 summit, a pivotal gathering comprising major economies from around the globe. The grand event unfolded in September in New Delhi, representing a significant milestone in India’s diplomatic efforts. With participation from leaders of all the prominent nations, it emerged as one of the most consequential international congregations in India’s history. The overarching theme, “One Earth, One Family, One Future,” underscored India’s commitment to fostering unity and cooperation on a global scale. In pursuit of inclusivity, India meticulously orchestrated over 200 meetings held across 60 cities throughout the country, ensuring diverse voices were heard and considered in the deliberations.
At the core of the summit lay the New Delhi G20 Leaders’ Declaration, a collective agreement endorsed by all member states, delineating a comprehensive strategy to address pressing global challenges. India’s emphasis on equitable and inclusive solutions resonated strongly within the declaration, reflecting the nation’s steadfast commitment to promoting fairness and solidarity among nations. Prime Minister Modi’s impassioned plea for peaceful dialogue over conflict echoed throughout the proceedings, reinforcing the importance of diplomacy and cooperation in resolving international disputes.
The summit witnessed an unprecedented influx of attendees, with over 100,000 participants converging from across the globe. This inclusive gathering comprised heads of state, ministers, and delegates from a multitude of nations, demonstrating the widespread recognition and support for India’s leadership in the global arena. Leveraging the collective efforts of various states and territories, India showcased its cultural richness and hospitality, offering a glimpse into its diverse heritage through culinary delights and vibrant performances.
ASEAN (Association of Southeast Asian Nations)
India’s “Act East Policy” is a strategic initiative that goes beyond geographical proximity. It focuses on strengthening ties with ASEAN countries, recognizing their economic dynamism and strategic significance. Through this policy, India collaborates with ASEAN on various fronts:
Trade and Economic Integration: The ASEAN-India Free Trade Agreement (AIFTA) aims to boost economic ties. It facilitates the flow of goods, services, and investments between India and ASEAN nations. By reducing tariffs and non-tariff barriers, AIFTA enhances economic integration.
Security Cooperation: India and ASEAN engage in joint efforts to counter transnational threats such as terrorism, piracy, and cybercrime. Regular dialogues and joint military exercises strengthen security cooperation.
Connectivity: Infrastructure development, including road networks, ports, and air connectivity, is a priority. Initiatives like the India-Myanmar-Thailand Trilateral Highway and the Kaladan Multi-Modal Transit Transport Project enhance connectivity within the region.
Cultural Exchanges: India promotes cultural diplomacy through festivals, academic exchanges, and people-to-people interactions. These exchanges foster mutual understanding and strengthen historical ties.
SCO (Shanghai Cooperation Organization)
India’s full membership in the SCO provides a platform for engagement with Central Asian countries and China. Key aspects include:
Regional Security: The SCO focuses on combating terrorism, separatism, and extremism. India actively participates in joint counterterrorism exercises and shares intelligence with member states.
Economic Cooperation: The SCO facilitates economic collaboration through forums like the SCO Business Council. India seeks to enhance trade, investment, and connectivity within the region.
Cultural and Educational Ties: India promotes cultural exchanges, academic cooperation, and people-to-people contacts. The SCO University network encourages educational linkages.
SAARC (South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation)
SAARC aims to promote regional cooperation among South Asian countries. India’s engagement includes:
Poverty Alleviation: India collaborates with other SAARC members to address poverty, hunger, and social inequality. Initiatives like the South Asian Food Bank aim to ensure food security.
Healthcare and Education: SAARC Health Ministers’ meetings focus on health challenges such as communicable diseases and maternal health. Educational exchanges enhance knowledge sharing.
Disaster Management: India actively participates in SAARC’s disaster management mechanisms. Cooperation during natural disasters strengthens regional resilience.
BIMSTEC (Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation)
BIMSTEC connects countries around the Bay of Bengal. India’s engagement includes:
Trade and Investment: BIMSTEC aims to boost intra-regional trade. India collaborates with member states on trade facilitation, investment promotion, and economic integration.
Energy Cooperation: India explores energy linkages, including hydroelectric power projects and cross-border electricity trade. Energy security is a shared concern.
Tourism and Cultural Ties: BIMSTEC promotes tourism, cultural exchanges, and people-to-people connectivity. India’s northeastern states benefit from improved connectivity with neighboring countries.
International Solar Alliance (ISA)
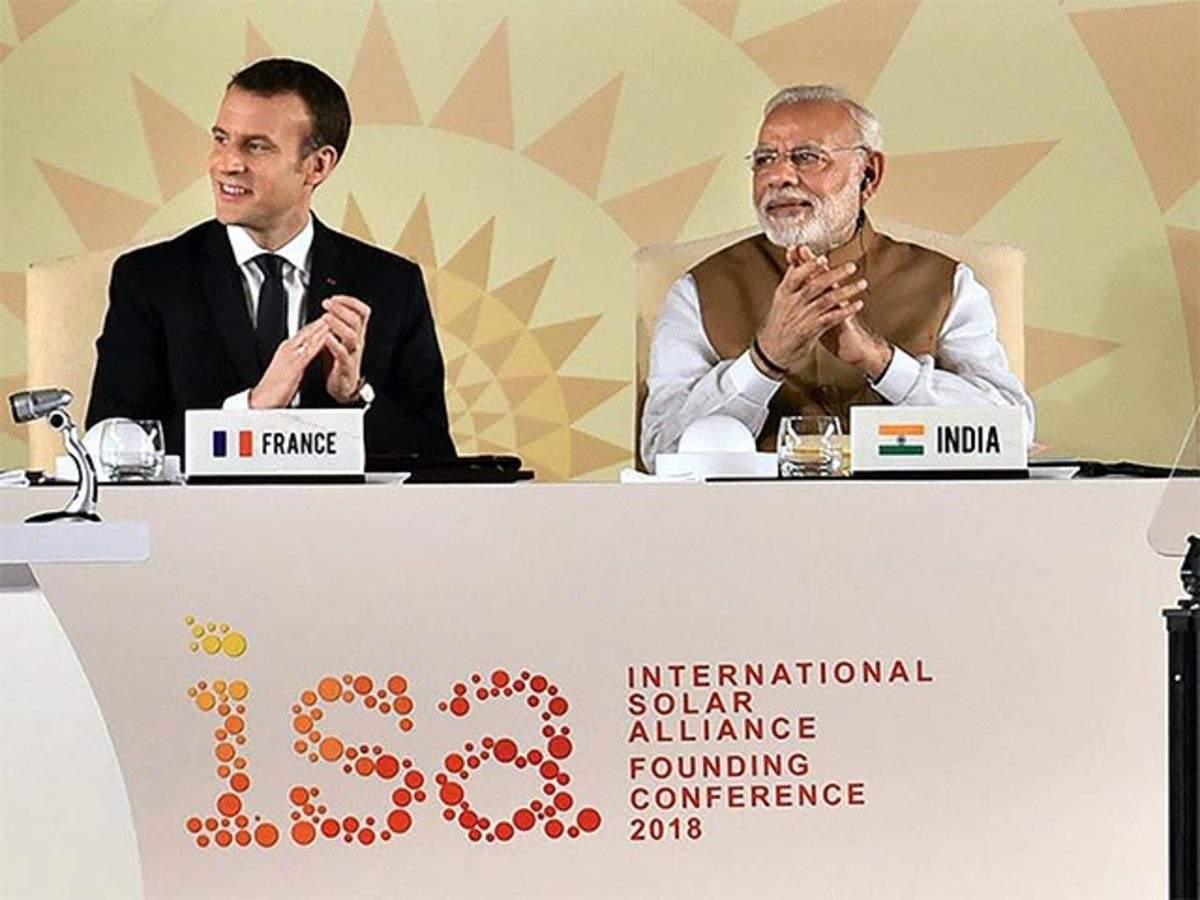

The International Solar Alliance (ISA) is a collaborative effort co-founded by India and France. Its primary objective is to promote solar energy adoption globally. The ISA brings together countries committed to clean energy solutions and climate action. By fostering cooperation, knowledge sharing, and technology transfer, it aims to accelerate the adoption of solar power. Through initiatives like the Solar Risk Mitigation Facility and the ISA Framework Agreement, member countries collaborate on solar projects, research, and capacity building.
United Nations (UN)
India holds a significant position as a founding member of the United Nations (UN). The UN serves as a global platform for addressing critical issues related to peace, development, and human rights. India actively participates in various UN bodies, including the General Assembly, the Security Council, and specialized agencies like the World Health Organization (WHO) and the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). India’s candidature for a permanent seat in the UN Security Council reflects its commitment to multilateralism and its role in shaping global governance.
Permanent membership of the United Nations Security Council
India has made persistent efforts towards securing a permanent seat on the United Nations Security Council (UNSC). The UNSC currently comprises five permanent members (Russia, the UK, China, France, and the United States) and 10 non-permanent members. India, along with Brazil, South Africa, Germany, and Japan, contends for permanent membership. These countries recognize the need to reflect the contemporary global reality in the UNSC’s composition. The ongoing Inter-Governmental Negotiations (IGN) process addresses various aspects of reform, including categories of membership and issues related to the veto power.
India has actively engaged in diplomatic efforts to reform the UNSC. The government consistently takes up the issue of UNSC reform with other member countries. Four out of the five permanent members of the UNSC have officially expressed support for India’s candidature, demonstrating growing international recognition of India’s global significance. China remains the only country that has not yet supported India’s bid for permanent membership. However, India continues to engage with China on this matter, emphasizing the need for reform.
India collaborates with other reform-oriented countries through its membership in the G-4 (India, Brazil, Germany, and Japan). Together, they advocate for UNSC reforms. The G4 nations propose a model that includes new permanent members elected democratically by the General Assembly. This model aims to change the balance of power dynamics within the UNSC. India’s position as the voice of the Global South strengthens its case for permanent membership. It actively promotes reformed multilateralism and advocates for greater representation and participation of developing countries.
India’s quest for permanent membership extends beyond symbolism. It seeks to redefine power dynamics and influence decision-making in global politics. While the road to permanent membership is challenging, India remains committed. It recognizes that hard work, mounting pressure, and collaborative proposals are essential to achieving this goal. As the UN faces perceived weakening, opportunities for India’s bid increase. The world increasingly acknowledges India’s democratic achievements, economic resilience, and role as a model for other developing nations.
Strengthening the Diplomatic Cadre and Outreach
India’s diplomatic efforts have witnessed significant developments, both in terms of strengthening the diplomatic cadre and expanding outreach.
Diplomatic Cadre Strengthening
The Indian government has taken steps to enhance the effectiveness and capacity of its diplomatic corps. Expansion of the Indian Foreign Service (IFS): The Union Cabinet approved a cadre review and restructuring of the IFS, creating 215 new positions over the next five years. This move addresses the increasing demand for specialized manpower and aims to meet the growing needs of existing missions and the planned opening of new Indian Missions.
Manpower and Funding: A parliamentary panel has emphasized the need to allocate sufficient resources to the Ministry of External Affairs (MEA). The committee recommends allocating at least 1% of the overall budget to support India’s extensive diplomatic outreach and foreign policy objectives.
Diplomatic Outreach
COVID-19 Pandemic Response: Amid the global pandemic, India’s diplomatic outreach has been active. India emerged as a major pharmaceutical supplier to the world, providing essential medicines and vaccines. Additionally, India extended humanitarian and disaster relief assistance to other countries, positioning itself as a responsible global player during the crisis.
International Solar Alliance (ISA): India co-founded the ISA with France to promote solar energy adoption globally. By fostering cooperation and technology transfer, the ISA contributes to sustainable development and climate action.
Strategic Engagements with ASEAN Nations: India actively engages with ASEAN countries through diplomatic channels. External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar’s recent visits to Singapore, Malaysia, and the Philippines underscore India’s commitment to regional cooperation. In Manila, Jaishankar expressed support for the Philippines’ sovereignty in the face of tensions with China in the South China Sea.
Conclusion
India’s foreign policy has undergone significant transformations, positioning the nation as a formidable global player. Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s strategic vision has propelled India’s standing on the international stage. As External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar aptly stated, “Asia is being shaped largely by the outlook of the US, the power of China, the weight of Russia, the collectivism of ASEAN, the volatility of the Middle East, and the rise of India.” This nuanced approach combines economic levers, soft power, and enlightened national interest. PM Modi’s emphasis on good governance, economic growth, and last-mile delivery has amplified India’s validity as a contender for a seat at the United Nations Security Council, reinforcing its role as the voice of the global south. In this complex interdependent world, India’s foreign policy success lies in its ability to wield both hard and soft power effectively, making it a strong force to reckon with.
The CSR Journal
CSR initiative launches #SmokinNot Campaign on World Health Day
Gurugram, India: BluSmart, India’s leading born-electric, full stack, vertically integrated eMobility ride hailing service and EV charging infrastructure network, collaborated with the Lung Care Foundation (LCF), a social impact trust dedicated to the cause of promoting lung health in India for the launch of #SmokinNot campaign on World Health Day. The month-long campaign is designed to encourage responsible ridership and aligns with BluSmart’s mission to ‘Decarbonise Mobility at Scale’ while fostering a healthier commute experience for both riders and driver partners.
The #SmokinNot campaign kick started on World Health Day on April 7, where Doctors from LCF trained and committed to advocate for Clean Air and Climate Action hosted an informative session for BluSmart Driver Partners at one of the BluSmart EV charging superhubs. As part of the awareness program, the roll out will include communication inside BluSmart EVs and in-app notifications to riders to spread the message of smoke-free, clean and healthy air both inside and outside EVs. BluSmart aims to create a cleaner travel experience, particularly in mega-cities of Delhi and Bangalore grappling with rising air pollution levels.BluSmart cab sticker
Sharing thoughts on the campaign, Anirudh Arun, Co-founder & CEO, BluSmart Fleet said, “BluSmart is committed to be smoke-free both within and outside of our EVs. Aligning with our mission to create a cleaner, more sustainable future, we encourage responsible and smart behavior among our driver partners and riders. With this year’s World Health Day theme being ‘My Health, My Right’, this campaign is designed in keeping the best interest of our Driver partners and our riders empowering them to choose a better lifestyle.”
Emphasising the urgency of the issue, Dr Arvind Kumar, Chairman, Institute of Chest Surgery, Chest Onco Surgery and Lung Transplantation Medanta; Founder and Managing Trustee Lung Care Foundation said, “We can’t wait any longer. The air we breathe and the choices we make have a profound impact on our health. It’s time to break free from the grip of air pollution and smoking. This initiative isn’t just about a clean car, it’s about taking a stand for a healthier future, for ourselves and for generations to come. Let’s breathe easy, drive smart, and create a world where clean air isn’t a privilege, but a civil right.”
“This collaborative endeavour aims to strengthen the contribution of citizen stakeholders to co-create and sustain the promotion of clean air and lung health for everyone. BluSmart’s efforts of reducing ambient air pollution coupled with the Driver partner’s efforts of maintaining a clean and fresh car cabin shall enthuse the guests to contribute too by keeping it smoke-free. Simple, small actions collectively lead to widespread awareness and impact” added Rajiv Khurana, Founder-Trustee, Lung Care Foundation.
Disclaimer: This media release is auto-generated. The CSR Journal is not responsible for the content.
CSR: Job Fair hosted for trained Solar Module Technicians in Bikaner
ENGIE India, a leader in low-carbon energy solutions, in collaboration with the National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC), trained over 600 students over a period of 2 years from Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, and Rajasthan as Solar Module technicians, recently ENGIE hosted a Job Fair for the students of Rajasthan, in Bikaner, Rajasthan.
The event focussed on felicitating talented individuals, equipping them with the knowledge and expertise to become Solar PV Installers (Suryamitra). The felicitation ceremony at the event honoured the students’ accomplishments upon successfully completing their Solar PV Installer training. This initiative reflects ENGIE India’s commitment to fostering a skilled workforce and promoting a sustainable energy future. By equipping individuals with job-ready skills and facilitating their entry into the green job market, ENGIE India is contributing significantly to India’s clean energy transition.
The felicitation and the job fair provided a platform for these graduates to connect with potential employers and explore career opportunities within the flourishing solar energy industry. This holistic approach ensured that the students gained the necessary skills and were well-positioned to secure employment in their field.
The project, undertaken by ENGIE Energy India Private Limited aimed to promote economic security and stability among youth by providing skill training and comprehensive development opportunities.
Amit Jain, CEO and Country Manager, India, echoed the company’s commitment to the initiative, stating, “Through such initiatives, ENGIE India remains dedicated to empowering young people, recognizing them as the architects of tomorrow. By providing opportunities for skill development and fostering a culture of inclusivity, we aim to equip young minds with the tools they need to shape a brighter, more sustainable future.”
Amit added, “this dedication extends beyond just initiatives. ENGIE India is committed to supporting the communities where we operate. We believe in building a strong local workforce and prioritize employing local talent. In fact, 80% of our staff across all our sites are recruited from within the local communities. This not only injects valuable skills and knowledge into our operations but also fosters a sense of community partnership.”
The informative and engaging event had participation from Mahindra Teqo and Sterling and Wilson who have also joined ENGIE in this cause by setting up booth for job fair. The event was organised to highlight the students’ accomplishments and provide them with opportunities to interact with industry experts.
With a portfolio of over 2.4 GW, with 1.1 GW already operational across seven states and another 1.25 GW in development, ENGIE has achieved considerable success spread across 20 projects strategically located in key Indian states.
Disclaimer: This media release is auto-generated. The CSR Journal is not responsible for the content.
Top CSR Projects in Hyderabad
The city of Hyderabad is known for its food, culture and development. The prosperity in the city has led many corporates to invest there, thus bringing the city under the purview of the CSR spending of the corporates.
In the FY 2021-22, the district of Hyderabad received the highest share of total CSR funds spent in the state of Telangana. The district’s share of CSR expenditure amounted to Rs. 386.21 crore from a total of 705 companies. The top three areas of focus of CSR projects in the districts were Education, Healthcare and Environment & Animal Welfare with Rs. 170.75 Cr., Rs. 154.53 Cr., and Rs. 30.05 Cr. spent respectively for them.
Top Companies for CSR in Hyderabad
The top three companies for CSR in Hyderabad in FY 2021-22 have been Tech Mahindra Limited, Aurobindo Pharma Ltd and Hindustan Aeronautics Limited.
CSR of Tech Mahindra Limited
Tech Mahindra is the part of the Mahindra Group, founded in 1945. The Mahindra Group has a clear focus on leading ESG globally, enabling rural prosperity and enhancing urban living, with a goal to drive positive change in the lives of communities and stakeholders. Tech Mahindra offers innovative and customer-centric digital experiences.
Founded in the year 2006, Tech Mahindra Foundation is the Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) arm of Tech Mahindra Limited. Their vision is ‘Empowerment through Education’ with three key focus areas – Education, Employability, and Disability.
All Round Improvement in School Education (ARISE)
ARISE or All-Round Improvement in School Education is our one-of-a-kind CSR education programme that aims to enable children from marginalised socio-economic strata with quality primary education and optimize their best potential. Focusing towards improving the quality of education in government and aided schools, the programme works in collaboration with various municipal corporations and state government bodies to develop primary schools into model schools of excellence.
At present, Tech Mahindra Foundation is working with schools affiliated to Greater Chennai Corporation, Pune Zilla Parishad Education Department, Telangana Education Department, and Anekal Education Department (in Bengaluru, Karnataka) to enhance quality education in government-run primary schools.
Shikshaantar
‘Shikshaantar’ aims to create a difference in education. Shikshaantar is the Foundation’s flagship training programme for school stakeholders including teachers, educators, school administrators and leaders to unleash their best potential for creating safer and happier classrooms. It also emphasises on the integration of physical, mental, social and emotional well-being of the students and teachers alike.
The Foundation runs the Shikshaantar program in two modes- in collaboration with partner organisations and through direct implementation. Established in 2017, one of the partner-implemented programs- ‘Science Academy’ in Hyderabad with Sahayata Trust that has trained a total of 1000 science teachers till date. Also, the Foundation runs various short-term modules for training on specific skills like ‘English-Winglish’ that aims to enhance English communication skills amongst teachers. Similarly, a teacher capacity building initiative in collaboration with Rotary India Literacy Mission was started during the pandemic to enhance their digital skills.
CSR of Aurobindo Pharma Ltd
A fully integrated pharma company, Aurobindo Pharma features among the top pharma companies in India. Aurobindo exports to over 150 countries across the globe with more than 90% of its revenues derived from international operations. Aurobindo Pharma Foundation is the philanthropic arm of Aurobindo Pharma Limited and strives for the social and economic growth of the nation through its Corporate Social Responsibility programme.
Eradicating malnutrition
The company has been working to combat widespread malnutrition, particularly among children and women, through several nutrition projects. Its newly established kitchen in Mahabubnagar district Telangana, as well as kitchens in Srikakulam in Andhra Pradesh and Narsingi (Hyderabad) Telangana, have provided approximately 9.50 crore meals through various avenues and programmes that feed government school students, farmers, daily wage labourers, and others.
A new programme called Swasthya Ahara has been launched through the Mahabubnagar kitchen, for serving hot healthy breakfast to 150 government schools near the kitchen.
Women empowerment
In the adopted model villages of Peyyalapalem in Nellore district, Andhra Pradesh state, and Borapatla in Sangareddy district as well as in Hyderabad district, Telangana state, the company has taken up various women empowerment programmes. The purpose is to positively impact the rural women and improving their livelihood opportunities. This aims to provide tailoring training programmes for women in order to assist them in boosting their income.
Cancer care
Cancer patients in Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, and neighbouring states will be able to obtain quality cancer treatment and healthcare at no cost with opening of the new oncology block at MNJ Institute of Oncology & Regional Cancer centre, Hyderabad, Telangana (capacity of 1,000 out-patients per day).
CSR of Hindustan Aeronautics Limited
Hindustan Aeronautics Limited is a state-owned aerospace and defence company. Headquartered in Bengaluru, HAL is one of the oldest and largest aerospace and defence manufacturers in the world.
In FY2021-22, the company spent Rs. 78.27 crores on its CSR activities and deposited Rs. 3 crores in the unspent CSR account against its mandatory CSR budget of Rs. 81 crores.
HAL has been undertaking CSR Projects in the local areas of its operations with a view to improving the quality of life of the socially & economically backward groups and marginalised & weaker sections of society. The main areas of focus of the company’s community development initiatives are infrastructure development, education, drinking water, river rejuvenation, environmental conservation, healthcare, sanitation, renewable energy, skill development, and sports.
The Company was accorded third prize in “National Water Awards” – 2020-21 under the “Best Industry for CSR activities” category instituted by the Ministry of Jal Shakti, Department of Water Resources, River Development and Ganga Rejuvenation.
Education and Skill Training
The company has established an Industrial training institute (ITI) for girls at Ghatkesar Mandal in Medchal – Malkajgiri District adjacent to Hyderabad. HAL also constructed Telangana Social Welfare Residential School & Degree College for girls in Medchal – Malkajgiri District.
Healthcare
HAL provided for supply of equipments and accessories for liver transplantation, plastic surgery & neuro surgery departments of Osmania General Hospital, Hyderabad.
Environment Sustainability
Upon request from Greater Hyderabad Municipality Corporation, the company spent for Conversion of Bio Waste to Compressed Natural Gas (CNG).
Drinking Water
Projects have been undertaken by HAL to provide Safe Drinking Water through Open Wells and Tube Wells. Depending upon the quality of water, Reverse Osmosis (RO) systems are also provided in schools and villages. Sumps and Overhead Tanks have been constructed and pipelines are laid up to a common point in the streets at select villages. Murali Nagar (Village) in Ranga Reddy District, Telangana was adopted by HAL, Hyderabad Division on the recommendations of the District Administration, Ranga Reddy District, Government of Telangana. The water available in the village is contaminated with fluorine which is causing bone related diseases. Hence, a community based RO Plant was provided and 20 liter water per day per family is being supplied to the families through Automatic Machine through card swiping. Similarly, Water ATMs have been provided at various villages of Niphad Taluka at Nasik, Maharashtra.
Other companies making an impact through CSR Projects in Hyderabad
Code Unnati CSR programme for skilling students
SAP Labs India’s CSR initiative, Code Unnati, which promotes skill development and employability among the youth in Industry, recently announced expansion into Telangana. Implemented by Edunet Foundation and supported by Telangana Academy for Skill and Knowledge (TASK), this expansion marks the establishment of centres of excellence dedicated to emerging technologies in 17 locations across the state.
The Code Unnati programme underscores the importance of industry-relevant skills in preparing individuals for the future of work, eventually creating pathways towards employability and future readiness for both faculty and students. The inaugural event was held on March 14, 2024, at Telangana Academy for Skill and Knowledge’s Regional Centre in Hyderabad.
SAP started this programme for students from economically weaker sections of the society, studying in Tier 2 and Tier 3 colleges. The 300+ hours’ Code Unnati program equips the colleges with SAP centres of excellence to enable experiential learning of deep tech. With elements such as capstone projects, mentoring, and capacity building of faculty, the program uses a sustainable hands-on approach towards levelling up the skills of underserved students and establishing a pathway to industry.
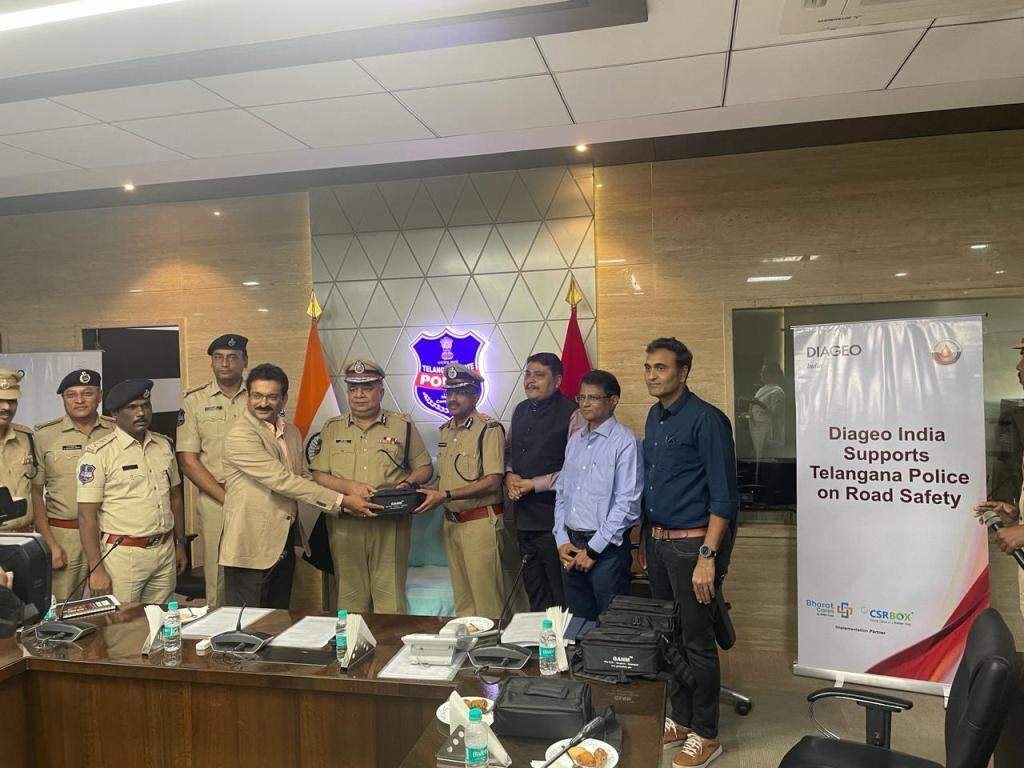
CSR support to Telangana Police to curb drunk driving
Alco-bev company Diageo India (United Spirits Ltd.) extended its support to Telangana Police in curbing drink driving by providing 50 advanced Alcohol Breath Analysers in February this year, the company said in an announcement. Diageo India drives focused programs to advocate for anti-drink driving through its flagship programme, ‘Wrong Side Of The Road’ which uses a series of real-life scenarios to create awareness among adults. The programme has been developed together with the United Nations Institute for Training and Research (UNITAR) to sensitize participants on the effects of drink driving. Diageo India has also partnered with over 25 Regional Transport Offices and set up tab labs to create awareness through the ‘Wrong Side of the Road’ programme. Last year over 2.3 lac adults participated in this anti-drink driving learning experience, the company said in a statement.

CSR of Gland Pharma Limited
The Company conducts its CSR initiatives through Gland Fosun Foundation. The main areas of focus of CSR initiatives of the company include Education, Good Health, Safety, Conservation of the Environment, Eco-Systems and Natural Resources.
Healthcare – In February 2021, in association with a healthcare provider, Gland Pharma conducted a ‘Comprehensive Health Plan’ for about 2000 socio-economically children from 26 government schools and orphanages in Hyderabad, to help them grow and develop to their full potential. After being screened through diagnostic tests, the children were counselled by health professionals on nutritional aspects and treated with suitable supplements. The company has also contributed to LV Prasad Eye Institute (LVPEI) for the setting up of a dedicated ‘Centre for Elderly Eye Care’ at Hyderabad. Inaugurated on 1st June 2021, the Centre will provide diagnostic and treatment services to all those in need on a sustainable basis. Over the next three years, it will also provide surgical services for at least 3,500 people, as well as house-to-house screening services for 5,000 aged people. In December 2020, the company made a contribution to Lions Eye Hospital (Moula Ali, Hyderabad), to help them set up a ‘Modular Operation Theatre’ in their new Surgical Wing, thereby expanding their outreach to those in need of surgical procedures.
Education – In November 2019, Gland Pharma launched a first-of-its-kind ‘Free Breakfast Scheme’ for nearly 9100 children of 66 government-run schools around our manufacturing facilities in Hyderabad and Visakhapatnam. These children begin their day with a nutritious breakfast prepared hygienically and supplied by Akshaya Patra Foundation. Hyderabad-based ‘Sannihita Homes’ is an NGO that runs four orphanages (three for girls and one for boys), looking after nearly 400 destitute orphans from vulnerable communities (badly abused backgrounds with no care / homeless / beggars / rag-pickers / migrant families). These destitute children are given shelter, food, education, healthcare and protection.
The company has undertaken to renovate these orphanages, in order to improve the living conditions of the orphans. It is also providing funding support to the NGO to help meet some of the NGO’s regular personnel and administrative expenses.
Wildlife Conservation – The Company contributed Rs 20 Lakhs to Nehru Zoological Park (Hyderabad) for the upkeep of its numerous wild birds and animals. It was warmly welcomed by the zoo authorities as well as several wildlife conservationists/animal lovers, who acclaimed it as a much-needed CSR gesture during this lockdown period when gate collections are badly depleted. Further in October 2021, it further donated Rs 20 lakh for the construction and maintenance of the kangaroo fence in Nehru Zoological Park.
Livelihood Development – Swayamkrushi is a Hyderabad-based NGO that shelters mentally challenged women and address their special needs through therapeutic services, music, yoga, speech and physiotherapy. It also 1) sensitises the community to the special needs of the mentally challenged, 2) works with families, the community, and voluntary and government agencies, and 3) run courses in Special Education and Caregivers’ Training. The company has extended its support to this NGO for:
– The construction of a ‘Vocational Training Centre-cum-Residential Block’ for the inmates
– The procurement and installation of a few jute bag-making machines.
Beautification of Charminar by NTPC
NTPC Ltd adopted the iconic Charminar in Hyderabad under the Swachh Iconic Places Projects of India. The company in collaboration with the Greater Hyderabad Municipal Corporation initiated the Charminar Pedestrianization Project, under which it committed to provide battery-operated vehicles for visitors, bollards to prevent traffic, Swachh Auto Tippers (SAT) for carting garbage, mechanical sweeping vehicles and litter picking machines, decorative and halogen lighting of four arches, construction of public utilities, toilets and drinking water ATM kiosks. The company committed to spending 8.19 Crores on this project.
World Health Day 2024: State government schemes for healthcare in India
World Health Day is celebrated on 7th April every year. Each year draws attention to a specific health topic of concern to people all over the world. The date of 7th April marks the Foundation anniversary of the World Health Organization (WHO), which was established in 1948. The theme for World Health Day 2024 is ‘My health, my right’.
Going with the theme, The CSR Journal takes a look into healthcare schemes offered by four states of India namely Odisha, West Bengal, Andhra Pradesh and Haryana to benefit citizens, especially those who are marginalised and less privileged.
While the Govt of Odisha offers Biju Swasthya Kalyan Yojana, West Bengal Government offers the Swasthya Sathi scheme, Andhra Pradesh Government is enhancing healthcare of its residents through the Aarogyasri scheme while on Haryana Day last year, the state government expanded the benefits of Ayushman/Chirayu scheme and introduced a cashless health facility for govt employees, pensioners and journalists.

Biju Swasthya Kalyan Yojana – Odisha
In December last year, Odisha Chief Minister Naveen Patnaik launched the third phase of the Biju Swasthya Kalyan Yojana (BSKY), the flagship health assurance scheme of his government, to cover rural poor families that were left out in the first two phases. Patnaik said with this third phase of expansion, it is estimated that over 1.10 crore families, covering nearly 90 per cent of the state’s population will be provided health assurance under BSKY. The chief minister said that the BSKY will ensure that no family in Odisha is left vulnerable due to lack of financial resources to meet high expenditure for critical illnesses.
As per the BSKY norms, the new beneficiaries will also be entitled to cashless care worth Rs 5 lakh per annum and the amount of coverage for women would be up to Rs 10 lakh in empanelled private hospitals both inside and outside the state. In the first phase of the BSKY, all services in public health facilities were made free of cost for all persons, irrespective of income or residence. In the second phase, BSKY provided cashless healthcare in private health facilities for all covered under Food Security Schemes and ration card holders. In the past five years, BSKY has provided free healthcare service to nearly 21 lakh patients with cashless healthcare of about Rs 4,500 crores, in private hospitals alone.

Swasthya Sathi scheme – West Bengal
Swasthya Sathi is a scheme that offers cashless hospitalisation up to Rs 5 lakh per family to those who cannot afford private healthcare across the state. The scheme was officially launched by Chief Minister of West Bengal Mamata Banerjee on 30th December 2016.
Main Features of the Scheme include basic health cover for secondary and tertiary care up to Rs. 5 lakh per annum per family. It is paperless, cashless and smart card based. All pre-existing diseases are covered. There is no cap on the family size and parents of both the spouse are included. All dependent physically challenged persons in the family are also covered.
The entire cost is borne by the State Government and no contribution from the beneficiary. Online Swathya Sathi Smart card is provided to each family on the day of Enrolment. Smart Card captures the details of the family members along with photographs, biometric, address, mobile number, caste ID etc. There is a 24X7 toll free Call Centre (18003455384) with feedback option along with Android based Swasthya Sathi Mobile app for assistance to the beneficiaries.
Swasthya Sathi covers 85 million people, providing up to Rs 500,000 in universal health insurance. The scheme helps around 7,000 people get treated at around 2,500 private hospitals and nursing homes every day, as per state government officials.

Aarogyasri scheme – Andhra Pradesh
The “Dr. YSR Aarogyasri Health Insurance Scheme” was launched in 2007 by the Govt. of Andhra Pradesh to provide financial aid to low-income families within the state. The scheme is a PPP model in the field of Health Insurance, tailor-made to the health needs of poor patients and provides end-to-end cashless services for identified diseases under secondary and tertiary care through a network of service providers from Government and private sector.
In December 2023, Andhra Pradesh government enhanced the coverage of its healthcare scheme for the poor, Dr YSR Aarogyasri, from Rs 10 lakh to Rs 25 lakh. Andhra Pradesh Chief Minister Y S Jagan Mohan Reddy said the revamped scheme will now provide free treatment costing up to Rs 25 lakh while expanding the coverage to about 4.25 crore people in the state under the purview of Aarogyasri. The treatment under the scheme is now being provided in 2,513 hospitals across the state, the Chief Minister said. The distribution of Smart Aarogyasri Cards with new features also started after the CM’s announcement of the upgraded scheme.
The state government bears the medical expenses for Aarogyasri card holders once their hospital bill crosses Rs 1,000. The state-sponsored health insurance scheme, meant to provide universal health coverage to BPL (Below Poverty Line) families, is run by the Dr YSR Aarogyasri Health Care Trust, in consultation with insurance and healthcare specialists. It includes a network of service providers from the government and private sector.

Ayushman/Chirayu scheme and cashless health facility for govt employees – Haryana
On the occasion of Haryana Day, 1st November, 2023, Former Chief Minister Manohar Lal Khattar launched two initiatives enhancing healthcare for residents of the state. The former Haryana CM extended coverage of the Ayushman/Chirayu scheme to families with annual income ranging from Rs 1.80 lakh to Rs 3 lakh. Earlier the scheme benefitted only families with an annual income below Rs 1.80 lakh. After expansion, the scheme will now benefit an additional 38,000 families.
On the occasion, another healthcare initiative was rolled out. This is a cashless health facility for government employees, pensioners, and accredited journalists and the entire expenditure under the scheme will be borne by the state government. Under this scheme, cashless treatment can be availed for 1,340 diseases across 569 empanelled hospitals in Haryana. The initial phase incorporates 894 employees from the fisheries and horticulture departments, encompassing 1,055 disease packages and 305 hospitals. Future plans include the extension of this scheme to other departments within the state.
कितनी स्वस्थ है हमारे देश की स्वास्थ्य व्यवस्था? पढ़ें Healthy India की पोल खोलती ये इलेक्शन रिपोर्ट
हमारी सांसे उखड़ रही थी, हमारी आस टूट रही थी, हमारे जहन में लगातार सवाल उठता कि क्या धरती पर इंसान का अस्तिव्त खतरे में आ गया है। हम इलाज के लिए दर-दर भटक रहे थे। एक अस्पताल से दूसरे अस्पताल लेकिन जगह नहीं मिलती। अगर हम जिद करते तो स्ट्रेचर पर अस्पताल के बाहर पड़े रहिये। ना ऑक्सीजन मिल रहा था और ना डॉक्टर और ना ही दवाईयां। ये आलम था कोरोना काल में जब समूचे विश्व में कोरोना महामारी की घोषणा हुई और अचानक देश की स्वास्थ्य व्यवस्था चरमरा सी गयी। देश के Health System पर सवाल खड़े होने लगे कि India Health System कितना कारगर है अपने Citizen की देखभाल करने में। अपने विकासशील देश की तुलना अन्य विकसित देशों से करें तो हेल्थ, Health Infrastructure, Technology in Healthcare में हम तो आगे है लेकिन ये सुविधाएं आम जरूरतमंद तक कितनी पहुंचती है ये सवाल है। भारत के लोकतांत्रिक व्यवस्था में आम जनमानस की अपेक्षा रहती है कि केंद्र और राज्य सरकारें उनके कल्याण के लिए कम करें, शिक्षा, स्वास्थ्य, रोजगार के साथ-साथ रोटी, कपडा, मकान, सड़क, बिजली, पानी जैसी बुनियादी सुविधाएं आपको मुहैया कराएं वो भी मुफ्त। देश की सरकारें भी वोट पाने के लिए इन सब को लेकर लोकलुभावन वादे करती है। स्वास्थ्य को लेकर भी केंद्र सरकार ने अपने मेनिफेस्टो में इसका जिक्र किया था। BJP Manifesto in Lok Sabha Election 2019 में Making Healthcare Accessible, Strengthening Health Infrastructure, Immunization and Nutrition, Eliminating Tuberculosis पर जोर देते स्वास्थ्य व्यवस्था को सुधारने को लेकर कई उपाययोजना की बात कही थी। आज World Health Day 2024 है ऐसे में आइये समझते हैं इस लोकसभा इलेक्शन रिपोर्ट कार्ड (Lok Sabha Election Report Card) के जरिये India में Health Services का हाल कितना बदहाल और कितना बेहाल है।

भारत में बेहद निराशाजनक है स्वास्थ्य सेवा की स्थिति
किसी भी देश की तरक्की तभी संभव है जब उसके नागरिक सेहतमंद हों। जनता स्वस्थ हो, इसके लिए देश में Medical Services in India दुरुस्त होनी चाहिए, लेकिन भारत में स्वास्थ्य सेवा की स्थिति निराशाजनक है। भारत पर अपनी 140 करोड़ आबादी की सेहत का ख्याल रखने की बड़ी जिम्मेदारी है। अपने देश में अनेक बीमारियां मौजूद हैं जो गरीबी, अशिक्षा, जानकारी की कमी, साफ सफाई, स्वच्छता एवं सेहत के प्रति उदासीनता की वजह से फैलती हैं। भारत के अनेक अस्पताल और डॉक्टर गुणवत्तायुक्त इलाज मुहैया कराने के लिए विदेशों में भी प्रसिद्धि हासिल कर रहे हैं लेकिन इसके बावजूद भारत में अब भी स्वास्थ्य संबंधी अनेक समस्याएं मौजूद हैं। भारत में जीवन प्रत्याशा दोगुनी हुई है। शिशु मृत्यु दर महत्वपूर्ण रूप से घटी है। स्मॉल पॉक्स, पोलियो और कुष्ठ रोग लगभग जड़ से खत्म हो गए हैं। मगर भारत की जनता कुपोषण, स्वच्छता और संक्रामक रोगों से अब भी जूझ रही है। पर्यावरण प्रदूषण और जीवन शैली, शराब का सेवन, धूम्रपान, उच्च वसायुक्त खान पान तथा गतिहीन जीवन के कारण देश में मधुमेह यानी डायबिटीज, हृदय संबंधी दिक्कतों जैसे हार्ट अटैक एवं कैंसर जैसी बीमारियों की दर बढ़ी है। कई सामान्य सी लगने वाली बीमारियां भी महामारी का रूप धारण कर ले रही हैं या व्यापक स्तर पर भारतीय आबादी को प्रभावित कर रही हैं।

टीबी, मलेरिया और डायरिया जैसे बीमारियों से भी लोगों की हो रही है मौत
संक्रामक बीमारियों मसलन टीबी, मलेरिया, काला-अजार, डेंगू बुखार, चिकनगुनिया, Water Borne Diseases जैसे हैजा और डायरिया भारत में प्रमुख स्वास्थ्य संबंधी समस्या हैं। भारत में बीमारियों से होने वाली कुल मौतों में एक चौथाई मौतें डायरिया, सांस संबंधी दिक्कत, टीबी और मलेरिया के कारण होती हैं। इसके अतिरिक्त अनेक नई बीमारियों जैसे एड्स, इबोला विषाणु, एवियन जुकाम, एच 1 एन 1 विषाणु इत्यादि के होने का खतरा हमेशा बना रहता है। इस प्रकार अनेक सामाजिक और आर्थिक कारणों से स्वास्थ्य संबंधी असमानताओं के रहते भारत लगातार बीमारियों का बोझ डोल रहा है। ग्रामीण और शहरी क्षेत्रों की समस्या भी अलग-अलग हैं। जहां शहरों में खराब जीवन शैली के चलते Heart, Liver, Kidney से संबंधित बीमारियां असमय ही युवा वर्ग को भी बेहद तेजी से अपनी गिरफ्त में ले रहे हैं। वहीं ग्रामीण क्षेत्रों में संक्रामक बीमारियां का प्रभाव कायम है।

नहीं है पर्याप्त हॉस्पिटल ना ही है पर्याप्त डॉक्टर
भारत को आजाद हुए लगभग 77 साल हो गए लेकिन आज भी चिकित्सा के क्षेत्र में पर्याप्त सुविधाएं उपलब्ध नहीं हैं। भारत में अब तक तीसरी दुनिया की कही जाने वाली अनेक बीमारियां व्याप्त हैं, जो काफी पहले ही विकसित देशों से विलुप्त हो चुकी हैं। भारतीय आबादी का बड़ा हिस्सा बीमारियों से जूझता है और अस्पतालों में लंबी कतारों के साथ सुविधाओं का अभाव है। जहां अनेक परीक्षण उपकरण (Medical Diagnostic Equipment) पुराने पड़ गए हैं। अपने देश में अस्पतालों (Hospitals and Doctors in Indian) और डॉक्टरों की उपलब्धता जनसंख्या के घनत्व के हिसाब से कम है और सरकारी अस्पतालों में स्वास्थ्य सुविधाओं, आधारभूत संरचना, चिकित्सकों, कमरों, दवाइयों, कुशल व प्रशिक्षित नर्सिंग स्टाफ एवं अन्य सुविधाओं की कमी है। नाइट फ्रैंक की एक रिपोर्ट के अनुसार, प्रति 1,000 लोगों पर 3 Hospital Bed होनी चाहिए ऐसे में इस अनुपात तक पहुंचने के लिए भारत को अतिरिक्त 2.4 मिलियन (24 लाख) अस्पताल बिस्तरों की आवश्यकता है। फिलहाल भारत में अनुमानित 70,000 अस्पताल हैं, जिनमें से 63 प्रतिशत निजी क्षेत्र से हैं यानी ये प्राइवेट हॉस्पिटल है। इन्हीं आभावों के चलते अपने देश में निजी स्वास्थ्य क्षेत्र को विस्तार करने का मौका मिल गया जिसका गरीब लोगों से कोई वास्ता नहीं।
तुरंत इलाज और फ़ौरन सर्जरी के लिए भी है लंबी वेटिंग लिस्ट, इन Health Policy in India से बदलाव संभव
जिन गंभीर रोगियों को तुरंत इलाज अथवा सर्जरी की जरूरत होती है उन्हें भी अस्पताल में भर्ती होने के लिए लंबा समय लगता है। यहां तक पता चला है कि कुछ अस्पतालों में तो एक बिस्तर को एक साथ तीन मरीज तक साझा करते हैं। इससे दूरदराज की स्थिति समझी जा सकती है। विश्व स्वास्थ्य संगठन के अनुसार भारत परिवर्तन की प्रक्रिया से गुजर रहा है और वर्तमान में यहां के स्वास्थ्य क्षेत्र के समक्ष अनेक चुनौतियां हैं। इनमें स्वास्थ्य के स्तर में सुधार लाना, जनता को बीमारियों से बचाना, जनता की अपेक्षाओं के अनुरूप बेहतर जवाबदेही सुनिश्चित करना, स्वास्थ्य सेवाओं को सुलभ बनाना तथा इनकी गुणवत्ता, निरंतरता व स्थिरता को सुनिश्चित करना प्रमुख है। इन समस्याओं को प्राथमिक स्वास्थ्य केंद्रों और अस्पतालों में स्वास्थ्य सेवाओं की सुलभता, लोक स्वास्थ्य सेवा, कार्यक्रम, पर्याप्त स्टाफ, मेडिकल इंफ्रास्ट्रक्चर और तकनीकी सुविधाओं से हासिल किया जा सकता है। भारत में सरकारों ने स्वास्थ्य क्षेत्र में अनेक कदम उठाए हैं जिनमें राष्ट्रीय स्वास्थ्य नीति 1983 (National Health Policy), स्थानीय संस्थाओं को शक्ति प्रदान करने वाले संविधान के 73वें व 74वें संशोधन, राष्ट्रीय पोषण नीति 1993, राष्ट्रीय स्वास्थ्य नीति, भारतीय चिकित्सा, होम्योपैथी, दवा पर राष्ट्रीय नीति 2002, गरीब स्वास्थ्य बीमा योजना 2003, सरकार के सामान्य न्यूनतम कार्यक्रम 2004 में स्वास्थ्य को शामिल करना है। इनके अतिरिक्त राष्ट्रीय ग्रामीण स्वास्थ्य मिशन और सार्वभौमिक स्वास्थ्य योजना भी बारहवीं पंचवर्षीय योजना में शामिल हैं। Healthcare in India
ग्रामीण भारत में हेल्थ सुविधाओं की स्थिति भयावह है
3100 मरीजों पर मात्र एक बिस्तर समूचा भारत स्वस्थ समूह की बदहाली की मार झेल रहा है। यही वजह है कि ग्रामीण क्षेत्र में आम जनमानस या तो झोलाछाप डॉक्टर से इलाज करने के लिए मजबूर है या फिर झाड़फूक के जरिए अपनी बीमारियों से निजात पाने का प्रयास करते हैं। सरकारी डॉक्टरों की ग्रामीण क्षेत्रों में तैनाती होने के बावजूद भी गांव में नहीं जाते। वो शहरों में अपना मेडिकल सेंटर शुरू कर देते हैं। कहते हैं कि असली भारत गांव में बसता है मगर गांव के लोगों की सेहत का ख्याल रखने वाले चिकित्सा केंद्र 21 सदी के भारत में भी बदतर ही है। ग्रामीण क्षेत्रों में चलने वाले प्राथमिक स्वास्थ्य केंद्रों और सामुदायिक स्वास्थ्य केंद्र में मेडिकल एक्सपर्ट की काफी कमी देखी जाती है। ऐसे शहर और गांव के बीच एक ऐसी खाई बन गई जिसका परिणाम भविष्य में काफी भयावह हो सकते हैं। भले देश में तरक्की की कितनी भी दावे किए जाएं पर गांव में करीब 80 फ़ीसदी चिकित्सा विशेषज्ञों की कमी होना अपने आप में कई सवाल पैदा करता है। ऐसे में स्वस्थ भारत खुशहाल भारत कैसे बनेगा। ग्रामीण स्वास्थ्य सांख्यिकी 2021-22 की रिपोर्ट बताती है कि देश के ग्रामीण क्षेत्रों में सर्जन डॉक्टर की लगभग 83 फीसदी कमी है, बाल रोग विशेषज्ञों की 81 फीसदी और फिजिशियन की 80 फ़ीसदी की कमी है। यही हाल प्रस्तुति एवं स्त्री रोग विशेषज्ञों की है ग्रामीण क्षेत्रों में इसकी अमूमन 72 फीसदी की कमी है। इतना ही नहीं प्राथमिक स्वास्थ्य केंद्र पीएचसी की हालत भी ठीक नहीं है। शिक्षा और स्वास्थ्य देश में कमाई का जरिया बन चुका है हालांकि केंद्र सरकार ने कुछ ऐसे प्रयास किए हैं जिस जिससे ग्रामीण और गरीब लोगों तक सस्ती और बेहतर स्वास्थ्य सुविधाएं पहुंच सके। इसमें आयुष्मान भारत योजना (Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana) शामिल है जिसका उद्देश्य 50 करोड़ से अधिक लोगों को स्वास्थ्य सुविधा प्रदान करना है मगर आयुष्मान भारत योजना भी अपर्याप्त वित्त पोषण, स्वास्थ्य कर्मियों की कमी, अपर्याप्त आधारभूत संरचना की वजह से हांफते हुई नजर आ रही है।

स्वास्थ्य सेवाओं में सुधार यानी आर्थिक विकास में वृद्धि
किसी भी देश में स्वस्थ नागरिक उस देश के लिए एक बहुत बड़ी पूंजी मानी जाती है। नागरिकों के स्वस्थ रहने से देश की अर्थव्यवस्था को सीधे सीधे दो लाभ होते हैं। एक, देश के स्वस्थ नागरिकों की उत्पादकता तुलनात्मक रूप से अधिक रहती है। दूसरे, यदि नागरिक बीमार हैं तो उनको स्वस्थ रखने के लिए अधिक खर्च करना होता है, जो कि एक तरह से अनुत्पादक खर्च की श्रेणी में गिना जाता है, और बीमार नागरिकों की उत्पादकता तो कम होती ही है। इस बीच यदि देश में उत्तम दर्जे की स्वास्थ्य सेवाएं उपलब्ध हैं तो अस्वस्थ नागरिकों को जल्दी स्वस्थ कर पुनः उनकी उत्पादकता को बढ़ाया जा सकता है। जिसका सीधा लाभ उस नागरिक के साथ ही देश के आर्थिक विकास में सुधार के रूप में भी देखने में आता है। हाल ही के समय में, भारत में स्वास्थ्य सेवाओं में सुधार के लिए केंद्र सरकार द्वारा लगातार प्रयास किए जा रहे हैं और केंद्र सरकार द्वारा स्वास्थ्य क्षेत्र पर खर्च की जाने वाली राशि का बजट में प्रावधान लगातार बढ़ाया जा रहा है ताकि देश के नागरिक न केवल स्वस्थ रहें बल्कि यदि बीमार भी हों तो उन्हें उत्तम दर्जे की स्वास्थ्य सेवाएं उपलब्ध करायी जा सके एवं वे शीघ्रतिशीघ्र स्वास्थ्य लाभ लेकर अपने आप को आर्थिक गतिविधियों में संलग्न कर सकें।

Ayushman Bharat Yojana वरदान साबित हो रहा है Health Schemes in India
इसी संदर्भ में यहां केंद्र सरकार द्वारा लागू की गई आयुष्मान भारत योजना का उल्लेख किया जा सकता है। यह योजना अल्पकाल में ही गरीब वर्ग के स्वस्थ जीवन का आधार बन कर गरीबों-वंचितों के लिए वरदान बन गई है। आयुष्मान भारत योजना या प्रधानमंत्री जन आरोग्य योजना, भारत सरकार की एक स्वास्थ्य बीमा कवर योजना है, जिसे 23 सितंबर, 2018 को पूरे भारत में लागू किया गया था। इस योजना का उद्देश्य आर्थिक रूप से कमजोर नागरिकों अर्थात बीपीएल धारकों को स्वास्थ्य बीमा मुहैया कराना है। इसके अन्तर्गत आने वाले प्रत्येक परिवार को 5 लाख रुपए तक का कैशलेस स्वास्थ्य बीमा (Cashless Health Insurance) उपलब्ध कराया जा रहा है। भारत में केवल आयुष्मान भारत योजना को ही लागू नहीं किया गया है बल्कि देश में स्वास्थ्य सेवाओं को आसान और सुलभ बनाने के लिए भी केंद्र सरकार अन्य कई प्रयास कर रही है। जैसे अभी गत वर्ष केंद्र सरकार ने ‘ई-संजीवनी’ टेलीमेडिसिन सेवा को आयुष्मान भारत डिजिटल मिशन (एबीडीएम) के साथ जोड़ दिया है। इसका उद्देश्य भारत में मौजूदा डिजिटल स्वास्थ्य सेवाओं की दूरियों को कम करने और संबंधित पक्षों के लिए डिजिटल रास्ता बनाना है। वर्ष 2018 में प्रारम्भ की गई आयुष्मान भारत योजना के अंतर्गत टेली-परामर्श सेवा, 3 करोड़ टेली-परामर्श को पार कर गई है। वहीं, 23 सितंबर 2018 को शुरू हुई आयुष्मान भारत जन आरोग्य योजना के अंतर्गत अभी तक 21 करोड़ से अधिक परिवारों को आयुष्मान कार्ड प्रदान कर दिए गए है।

भारत मेडिकल टूरिज्म का हब बनता जा रहा है
यूं तो स्वतंत्रता प्राप्ति के बाद से ही देश में स्वास्थ्य सेवाओं में सुधार के लिए प्रयास किए जा रहे हैं परंतु पिछले 8-9 वर्षों के दौरान इस ओर विशेष ध्यान दिए जाने से देश की स्वास्थ्य व्यवस्था में व्यापक सुधार दृष्टिगोचर हुआ है। कोरोना महामारी के दौरान जिस तरीके से भारत में इस महामारी को सफलतापूर्वक नियंत्रित किया गया, इसकी पूरे विश्व में भारत की सराहना हुई है। 130 करोड़ से अधिक आबादी वाले देश में अन्य विकसित देशों की तुलना में मृत्यु दर बहुत कम रही और बाद के समय में तो भारत में ही तैयार किए गए टीके के भी 200 करोड़ से अधिक डोज देश के नागरिकों को सफलतापूर्वक लगाए जा चुके हैं, जिससे कोरोना महामारी एक तरह से भारत में नियंत्रित हो गई है, वहीं चीन, अमेरिका, ब्रिटेन, आदि देशों के नागरिक अभी भी कोरोना बीमारी से जूझ रहे हैं। भारत में न केवल स्वास्थ्य सेवाओं में सुधार हुआ है बल्कि भारत में चिकित्सा क्षेत्र के बुनियादी ढांचे को मजबूत बनाने में भी केंद्र सरकार ने अतुलनीय कार्य किया है, इसमें चिकित्सा सुविधाओं के विस्तार के साथ ही तकनीकी सुविधाओं का विस्तार भी शामिल है। इसके कारण आज विदेशी नागरिकों के इलाज के लिये भी भारत एक पसंदीदा जगह बनता जा रहा है। भारत मेडिकल टूरिज्म का हब बनता जा रहा है। मेडिकल सुविधाओं के मामले में भारत आज विश्व के कुछ चुनिंदा देशों में शामिल हो गया है। विदेशी नागरिक भारत में अब केवल घूमने के मकसद से नहीं आ रहे हैं बल्कि अपना इलाज कराने भी आ रहे हैं। हर साल जटिल बीमारियों का इलाज कराने लाखों विदेशी नागरिक भारत आ रहे हैं। भारत आज दुनिया में तीसरा सबसे बडा, इलाज के लिहाज से, पसंद किया जाने वाला देश बन गया है।
निष्कर्ष
भारत स्वास्थ्य चुनौतियों का सामना कर रहा है। जो नागरिकों की भलाई को प्रभावित कर रही है। भारत प्रमुख स्वास्थ्य समस्याओं से निपटने के लिए कई उपाय लागू किए हैं। जिनमें राष्ट्रीय स्वास्थ्य कार्यक्रम शुरू करना, स्वस्थ जीवन शैली को बढ़ावा देना और देश की जनता को सस्ती और सुलभ स्वास्थ्य सेवाएं प्रदान करना शामिल है। हालांकि इन स्वास्थ्य चुनौतियों से निपटने और सभी नागरिकों की भलाई सुनिश्चित करने के लिए और अधिक प्रयास किए जाने की जरूरत है जो कि भारत सरकार लगातार इसमें काम कर रहा है चाहे वह स्वास्थ्य सुविधाओं को बढ़ाने को लेकर या फिर मेडिकल हेल्थ इंफ्रास्ट्रक्चर को बढ़ाने को लेकर। इन स्वास्थ्य चुनौतियों के बारे में जागरूकता बढ़ाने, स्वस्थ जीवन शैली को बढ़ावा देने और विशेष रूप से दूर दराज और ग्रामीण क्षेत्र में स्वास्थ्य सेवाओं तक पहुंच में सुधार करने के प्रयास लगातार भारत सरकार द्वारा किया जा रहा है। इसके अलावा सरकार को पर्यावरण प्रदूषण, अपर्याप्त स्वच्छता और गरीबी सहित इन स्वास्थ्य चुनौतियों को मूल कारणों को संबोधित करने पर भी ध्यान सरकार दे रही है। इसके साथ-साथ हम सब मिलकर काम करें तो इन स्वास्थ्य चुनौतियों का समाधान कर सकते हैं और सभी नागरिकों के लिए एक स्वस्थ और अधिक समृद्ध भारत बना सकते हैं।
Loksabha Election Report Card on Health in India
Technology Trends That Are Encouraging Sustainability in The Luxury Real Estate Sector
Technology in real estate has traditionally focused on streamlining business processes and alleviating conventional challenges. However, there is a discernible shift as technology now assumes a more targeted role, specifically when it comes to sustainability and environmental consciousness. One sector where this convergence is increasingly evident is luxury real estate, where in addition to grandeur, technology is helping to redefine standards, not only for sophistication but also for a meaningful contribution to a sustainable and eco-friendly future.
The Need for Sustainability
According to the Economic Survey (2022-23), India’s economy is poised to grow at a rate of 6.5% in FY24. This growth is anticipated to escalate energy demand, particularly with the population projected to reach 1.5 billion by 2030. To ensure sustainability in this evolving scenario, there’s a pressing need for the real estate sector, which currently contributes to 22% of India’s energy demand, to integrate new technologies into its practices and figure effective solutions that minimise negative impact on the environment.
Smart Building Systems
Smart building systems integrate advanced technologies to enhance the efficiency and sustainability of structures. In luxury real estate, these systems play a pivotal role in reducing environmental impact and optimising resource usage. Examples include intelligent lighting and HVAC systems that adjust based on occupancy, natural light, and weather conditions, ensuring energy conservation.
Additionally, advanced building automation systems enable centralised control over various components, such as security, climate, and entertainment, promoting streamlined operations and energy efficiency. Smart meters and sensors provide real-time data, empowering homeowners to make informed decisions for sustainable living. Overall, smart building systems in luxury real estate contribute significantly to environmental sustainability by minimising energy consumption and promoting efficient resource utilisation.
Renewable Energy
Renewable energy, with a spotlight on solar power, is gaining traction as a potent force in curbing greenhouse gas emissions and combating climate change. Recent strides in battery technology have empowered the storage of renewable energy, paving the way for buildings to operate seamlessly on clean energy year-round.
Solar energy is making its mark in society operations, energising lifts, and illuminating common areas through solar panel roofs boasting a 25KW capacity. To facilitate the transition to renewable energy, guidelines such as The Greenhouse Gas Protocol have emerged, offering stakeholders and developers a roadmap to optimise energy usage. Strategies like Virtual Power Purchase Agreements (VPPAs), Green Energy Credits, Net Metering, and Green Tariff Mechanisms are being championed, encouraging the widespread embrace of renewable energy sources.
Water Conservation
Technology can also play an important role in advancing water efficiency. For instance, utilising real-time weather data and smart irrigation systems can adapt schedules for optimal efficiency. There are also other ways such as advanced leak detection mechanisms which can swiftly identify and alert, preventing potential wastage. Furthermore, high-tech, low-flow plumbing fixtures seamlessly integrate luxury with sustainability, effectively reducing water consumption.
There are also other very advanced and futuristic options such as automated rainwater harvesting systems equipped with sensors that optimise collection for non-potable uses like irrigation. All of these smart monitoring systems offer real-time insights, empowering informed decision-making by homeowners. Centralised platforms ensure a cohesive and efficient water management strategy in high-end homes, defining a sustainable paradigm in water usage.
Eco-Friendly Construction Materials
Technological advancements are also changing the landscape of eco-friendly construction materials. This transformative journey spans from energy-efficient appliances to innovative systems like geothermal heating. Among the notable eco-friendly materials is cellulose insulation, comprised of 75-80% recycled content, notably newspapers, providing a cost-effective and sustainable substitute for traditional fibreglass, while offering superior insulation and soundproofing benefits.
There is also an evolution in groundbreaking technologies like Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS), particularly in materials like concrete, showcasing the potential to significantly diminish carbon dioxide emissions from the construction sector, which currently contributes to about 39% of global energy-related CO2 emissions.
Simultaneously, the advent of sustainable construction materials sourced from renewable resources such as bamboo, hemp, and mycelium mark a notable shift towards materials with substantially lower carbon footprints when compared to conventional options like steel and concrete, aligning with the industry’s commitment to environmentally conscious practices.
The changing expectations of consumers have reshaped the definition of luxury in the real estate landscape. Beyond lavish finishes and expansive spaces, luxury now embraces sustainability, the seamless integration of technology, and a comprehensive approach to overall well-being. In response to this shift, developers are embracing green building practices, energy-efficient designs, and the inclusion of wellness amenities in their projects. The current trend in luxury home design prioritises the creation of environments that foster both physical and mental well-being.