ICICI Bank CSR shows a deep commitment to skill building for the larger purpose of Nation Building. Ranked the ‘Best Company to Work For’ fourth year in a row (by Business Today magazine), this bank is a large provider of financial services and products. The diversified portfolio caters to individuals as well as corporate customers.
It has a wide network of branches and ATMs but also believes in keeping up with the digital revolution. Apart from mobile and internet banking, this company is making financial services more inclusive, responsible and sustainable in India. Read our corporate social responsibility report on the bank to know how.
1. ICICI Bank CSR Overview
A laser-sharp focus on inclusive growth through strategic skill development programmes at the urban and rural level sums up corporate social responsibility at ICICI Bank. The organisation proactively acts as a catalyst for the socio-economic development of our nation, and considers this its main objective. This objective sets the tone for corporate citizenship programmes. These interventions are turning villages into self-sustaining ecosystems, women into self-reliant and equal participants in progress and empowering the marginalised sections to benefit from progress.
2. Leaderspeak
2.1. Girish Chandra Chaturvedi
 Mr. Chaturvedi, Chairman, writes: “There is a consensus among all stakeholders of business organisations that current or near term financial performance is not a sufficient indicator of the long-term prospects of a business. Stakeholders have begun to seek a deeper understanding of the sustainability of a business, around three broad areas: its impact on the environment and its ability to adapt to climate change; its impact on society, including fairness and equity in the treatment of customers and employees; and the effectiveness of its governance structure in ensuring that the business is conducted ethically and managed with a view towards long-term sustainability.
Mr. Chaturvedi, Chairman, writes: “There is a consensus among all stakeholders of business organisations that current or near term financial performance is not a sufficient indicator of the long-term prospects of a business. Stakeholders have begun to seek a deeper understanding of the sustainability of a business, around three broad areas: its impact on the environment and its ability to adapt to climate change; its impact on society, including fairness and equity in the treatment of customers and employees; and the effectiveness of its governance structure in ensuring that the business is conducted ethically and managed with a view towards long-term sustainability.
Appropriate oversight at the highest level of an organisation along with effective policies and practices are integral to effectively manage the wide variety of risks any business is faced with. A commitment to ethical conduct in all areas of operations and in the engagement with stakeholders is essential to build long-term trust in the franchise. A non-discriminatory approach towards customers and employees and a service-oriented culture are fundamental to contributing to the growth of businesses as well as society. Products and services should be designed to be fair to customers and should factor in the impact on society and the environment.
We have focused on ESG (environment, society and governance) through our governance framework, our approach to business and our CSR initiatives. In the area of environment, the Bank has financed projects for capacity creation in environment-friendly sectors. The Bank assesses social and environmental risks when evaluating new projects for financing.
The Bank’s business operations are conducted keeping in mind the environmental limits and ensuring ongoing efficiency gains. The Bank has also been ensuring green building features in all its large offices and new premises.
With regard to social responsibility, the Bank has endeavoured to have a transparent and ethical relationship with all its stakeholders. Being fair and ensuring right-selling of products has been a core element of the Bank’s strategy in its engagement with customers. The Bank has a no-discrimination approach in its treatment of employees.
Going beyond businesses, large organisations are also deploying their managerial expertise and financial resources in addressing socio-economic gaps through corporate social responsibility (CSR) related activities. We have a long-standing commitment to undertaking social initiatives that have a meaningful impact on society. Enabling access to banking and financial services in rural areas is a key focus area. This has been made possible by leveraging technology and working with a network of partners for providing last mile access. Economic empowerment of women is integral to the efforts of the Bank in rural areas.
ICICI Foundation for Inclusive Growth was set up in October 2008 and focuses on socially impactful and scalable projects, with funding from the Bank and its subsidiaries. Through its skill development activities, providing free training to youth and helping the trainees to find employment, the Foundation has created an opportunity for the youth to build an independent life and be part of mainstream economic activities. This has been further dovetailed with the rural strategy and the focus on strengthening rural ecosystems. Under its Rural Livelihoods initiative, ICICI Foundation has adopted a holistic approach to socio-economic development in rural areas. The strategy involves four pillars: leveraging and improving local skills and output; enhancing market linkages; facilitating low investment entrepreneurial opportunities; and addressing local environmental challenges by promoting sustainable practices.”
2.2. Saurabh Singh
 Mr. Singh is Head – TASC & GBG, ICICI Bank Limited and President, ICICI Foundation for Inclusive Growth. He writes: “The ICICI Foundation for Inclusive Growth has made a difference to over half a million lives in the country through sustainable livelihood. Scaling up has been in our DNA. We continuously strive to upgrade and enhance the lives of the lesser privileged and marginalised sections of society.
Mr. Singh is Head – TASC & GBG, ICICI Bank Limited and President, ICICI Foundation for Inclusive Growth. He writes: “The ICICI Foundation for Inclusive Growth has made a difference to over half a million lives in the country through sustainable livelihood. Scaling up has been in our DNA. We continuously strive to upgrade and enhance the lives of the lesser privileged and marginalised sections of society.
ICICI Academy for Skills has now empowered over 1,45,000 youth in the country. With 100% job placement of all trainees, we have achieved our goal of enabling them to earn a livelihood. In FY 2020 we trained and employed over 25,000 youth. With the opening of three new centres, in Aurangabad, Osmanabad and Jammu, we were able to address a large section of the less privileged. Today we operate with 27 academies across 20 states/union territories. Keeping updated with the dynamic needs of the industry, we have tied up with 11 knowledge partners who drive the content for our curriculum. We added one more technical course this past year: Service Technician Home Appliances. We are delighted to have Godrej and Boyce Manufacturing Company Limited on board as our knowledge partner for the same. Our quality classrooms and on-the-job training programmes have ensured that over 1,300 partners have recruited our trainees.
ICICI Rural Livelihood Programmes revolve around a four-point strategy of addressing shortage, surplus, inclusion and environment. We have made a substantial difference to more than 2,75,000 lives in creating sustainable livelihoods. Much of this has been in the areas of improving quantity and quality of produce, creating wealth from waste, providing sustainable livelihoods to landless farmers and protection of the environment. This has contributed significantly in strengthening ecosystems across the states in which we operate. In FY 2020 we further aligned to cluster-based models. The model has delivered tangible impacts across communities. Today our contributions are visible in more than 30 states/union territories, covering 115 clusters (over 2,100 villages).
ICICI Rural Self Employment Training Institutes in Udaipur and Jodhpur continue their focus on rural skill development targeted at local self-employment opportunities. ICICI RSETI Jodhpur, awarded as the best RSETI and ICICI RSETI Udaipur as the second-best among the 587 operational RSETIs in India. From inception, we have trained over 1,01,000 individuals. In the year 2020 we trained over 17,000 trainees. India’s first IGBC Platinum – rated net zero energy new building for ICICI RSETI Jodhpur, was inaugurated on September 11, 2019.
The COVID-19 pandemic has been unprecedented in this country. The foundation is committed to leaving no stone unturned while assisting the government in coping with this emergency. We are working closely with the central and state governments, the state police, healthcare and municipal workers, making sure that we monitor their needs. These include providing ventilators, hand sanitizers, gloves, 3-ply masks and PPE equipment essential for the safety and efficiency of frontline professionals. All our staff members have been sensitised to the need of the hour: ensuring safety for oneself as well as others by staying home and maintaining social distance protocols, sporting a mask when outside, etc. All our teams are working cohesively towards making the best use of technology in enabling remote working facilities.
None of this would have been possible without the support of our group companies, our employees and trainers, our knowledge partners, and the multitude of government institutions we have been engaging with for their continual support as we work towards furthering our shared vision of more inclusive growth.”
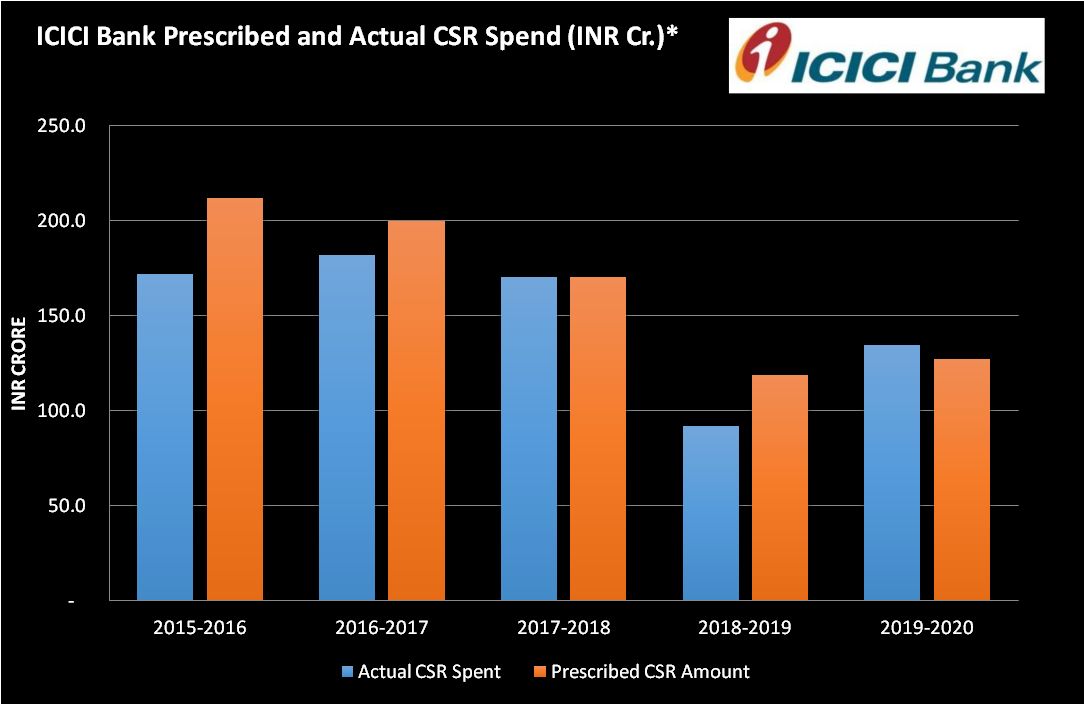
3. CSR spend
ICICI Bank CSR budgets have been fluctuating over the years. The actual spend was noticeably lower than the prescribed amount for the past few years, as you can see in the graph. The exception to this pattern was 2017-18 when the CSR spend matched the desired percentage from the profits. The latest figures have bucked the trend, with the company spending over Rs. 7 crores more than the prescribed budget on social initiatives. Perhaps the COVID-19 pandemic had a role to play in the steep rise. ICICI Group (of which the bank is a part) made a commitment of Rs. 100 crore towards relief measures after the outbreak. The bank’s contribution comprised more than half the pledge.
4. UN Sustainable Development Goals
ICICI Bank corporate social responsibility has attempted to align its ESG and CSR initiatives with the Sustainable Development Goals set down by the United Nations. Here’s a breakdown of how it’s trying to achieve the specific goals for the year 2030.
SDG 1 – No Poverty
ICICI Foundation, which executes many of the bank’s CSR programmes, has skilled 5.2 lakh impoverished persons so as to provide them a source of earning and take them out of the cycle of poverty. The organisation is not only bringing banking to the vast unbanked population (with 2.1 crore accounts), but has also lent to 70 lakh women who belong to SHGs (Self Help Groups) with SBLP so they can have a shot at cash flow and running their own businesses.
SDG 2 – Zero Hunger
Rural development is nothing without monetary aid to farmers who are the essential links in the agri-value chain. The corporate has designed various instruments to cater to their financial needs. One of these innovations is the app Mera iMobile. Available in 12 Indian languages, it has nuggets of information for the kisan, from real-time weather to prices of produce. This app can be used without an internet connection, reducing the burden on villagers who might not have internet connectivity.
ICICI Foundation runs rural livelihood programmes which not only teach sustainable agriculture but also develop the village as a whole. This initiative has impacted 2.75 lakh people in more than 2,100 villages.
SDG 5 – Gender Equality
The corporation employs a large number of women, since it’s an equal opportunity employer. Apart from various levels in the workforce, women have been occupying positions of leadership over the last two decades here. There are policies in place to ensure women’s safety and wellbeing, so they can work without fear of harassment.
The SBLP programme promotes gender parity by encouraging women entrepreneurs. ICICI Academy for Skills has been upskilling girls and young women for free, providing them placement opportunities when they complete training. More than half the trainees at the Academy are female.
SDG 8 – Decent Work and Economic Growth
ICICI Bank CSR runs skill development courses for people from low income backgrounds, affording them a chance for decent work. The courses are held at centres in 29 different states across the country. Rural banking takes financial literacy to women, farmers and micro-entrepreneurs.
5. Disaster Relief
The global pandemic was undoubtedly the biggest disaster last year. ICICI Group pledged Rs. 100 crores in support of COVID-19 relief measures in India. The Group directly contributed Rs. 80 crores to the PM CARES Fund, with the Bank donating Rs. 50 crores. Besides the donation, ICICI Foundation provided state and local governments with medical gear worth Rs. 20 crores.
Fake news proliferated in the early days of the outbreak, and still does. There was chaos about how to avoid getting infected. ICICI Bank corporate social responsibility teams called and texted 6.25 lakh people with precautions to take. ATM vans were plying the streets so that citizens could withdraw cash during the lockdown. The bank also aided the government in collecting donations digitally, since it has received a mandate for the central government’s PM CARES Fund and other state disaster relief funds.
6. Inclusive Banking
Financial inclusion and rural growth go hand in hand for ICICI Bank corporate social responsibility, hence the emphasis on financial literacy in the villages. Reaching out to the vast unbanked majority is part of the inclusive goal. They do this by identifying those who could become customers in the rural value chains. They encourage villagers to open their own savings account. A vast network of branches and digitally savvy individuals called Business Correspondents make this happen. They also help the rural poor make transactions easily.
9.1. Mera iMobile
Mera iMobile is an app that brings convenient banking at the fingertips of the rural and semi-urban folks. Launched in the year 2017, this mobile app is available in 12 regional Indian languages. Mera iMobile is not restricted to customers only; it can be used by anyone to find out about loans, real-time weather and make financial and non-financial transactions (nearly 1.68 crore of them were processed in 2020).
9.2. Financial Inclusion
The bank reached a new milestone in financial inclusion last year, opening the largest number of accounts for a private sector bank in the subcontinent; 2.1 crore basic savings accounts. It’s a financially inclusive milestone since 47 lakh of these were under the Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY). The bank supports various government schemes including life insurance scheme Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana, accident insurance scheme Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojana and pension scheme Atal Pension Yojana. Part of the financial literacy gamut is an MoU for spreading investor awareness with the Ministry of Corporate Affairs’ department IEPFA (Investor Education and Protection Fund Authority).
9.3. Micro-lending

Micro-credit or micro-lending is the lending of rather small loans to impoverished or fledgeling entrepreneurs. Micro-finance had many independent individuals as players in the rural economy but has recently witnessed more banks joining the fray. SBLP (Self Help Group-Bank Linkage Programme) is one such programme that works with women from Self Help Groups (SHGs) who want to become financially independent.
Apart from lending rural micro-entrepreneurs (especially women) small loans and opening zero-balance savings accounts for them, it also organises financial literacy camps. ICICI Bank corporate social responsibility has witnessed a gradual rise in women-led entrepreneurial ventures in its intervention areas. They have provided loans to over 70 lakh women beneficiaries. The team has partnered with 530 Self Help Promoting Institutions (SHPIs), which are empanelled as Business Correspondents and with Microfinance Institutions (MFIs).
7. Skill Development
Skilling is the main focus area of the strategic CSR of ICICI Bank. It has always believed that skill development can contribute leaps and bounds to Nation Building, a belief that has proven prophetic in the long run. ICICI Foundation runs various skill building programmes that have led to job placements for young people, especially women.
7.1. ICICI Academy for Skills