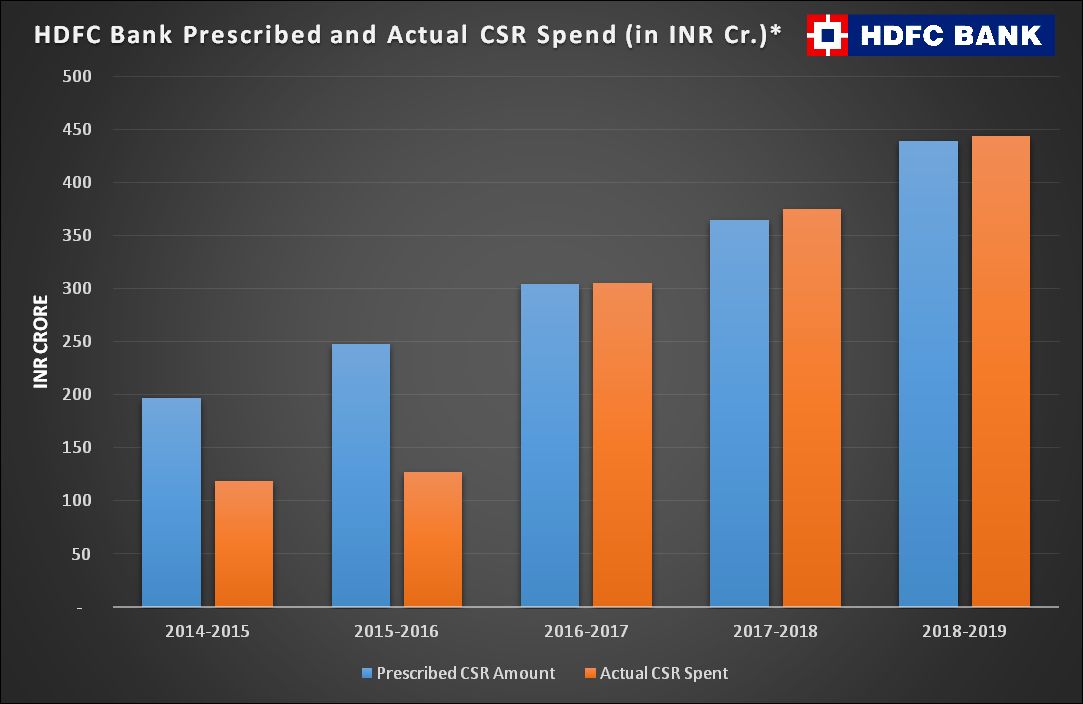
Much before corporate social responsibility (CSR) contributions were made mandatory by the Companies Act of 2013, HDFC Bank was following board-approved targets and contributing to social causes. HDFC Bank CSR spend was INR 443.8 crores during the year ending 31 March, 2019, bettering the FY18 performance by 20%, according to the company’s integrated Annual Report.
With a commitment of INR 150 crores to the PM-CARES fund, the HDFC Group also joined the fight against COVID-19. HDFC Ltd Chairman Deepak Parekh lauded the efforts of state governments and Centre and said the amount was to show its support to the battle against the deadly virus.
The Housing Development Finance Corporation Limited (HDFC Bank Ltd) commenced its operations as a scheduled commercial bank in January 1995 and is headquartered in Mumbai. It is currently India’s largest private sector lender.
The bank has a diversified network of business operations, which are split into domestic (India) and international operations. The banking services cover Commercial Banking, Investment Banking, Transactional Banking spread over wholesale and retail segments and treasury operations.
Watch a synopsis of HDFC Bank’s sustainability report in the video:
1. Parivartan – HDFC Bank CSR initiative
HDFC Bank Corporate Social Responsibility is implemented under the aegis of ‘Parivartan’ (the umbrella brand for all its social initiatives). HDFC Parivartan aims to bring about a transformation in the communities in which the Bank operates through initiatives in the sectors of Education, Skill training and Livelihood Enhancement, Health Care, Environmental Sustainability and Rural Development.
The CSR Policy (approved by the Board) is driven by the vision of ‘Creating Sustainable Communities’. The company’s CSR policy and programmes are aligned to comply with the requirements of Section 135 of the Companies Act, 2013 and are monitored by a Board-level committee.
2. CSR Policy
According to HDFC Bank CSR policy, its CSR mission is to contribute to the social and economic development of the community. It seeks to mainstream economically, physically and socially challenged groups in society, and to draw them into the cycle of growth, development and empowerment.
At the core of this mission are the Sustainable Livelihood Initiatives (SLI) that reach out to marginalized communities. The company’s corporate sustainability strategy is to integrate its activities in community development, social responsibility and environmental stewardship in such a way that encourages each business unit / function to include these considerations into its operations.
2.1. CSR Committee
In compliance with the guidelines of the Ministry of Corporate Affairs, the company has constituted a Board-level CSR Committee to govern the implementation of the CSR policy. The HDFC Bank CSR committee monitors the progress of CSR projects on a periodic basis. The HDFC Bank Corporate Social Responsibility committee comprises:
1) Mr. Umesh Chandra Sarangi, Chairman (Independent Director)
2) Mr. Aditya Puri
3) Mr. Malay Patel (Independent Director)
4) Mr. Sanjiv Sachar (Additional Independent Director)
2.2. HDFC Bank CSR Team
A dedicated CSR team drives all the CSR programmes with the guidance of senior functionaries, in particular, the Managing Director/ Deputy Managing Director. The CSR Committee and CSR team are entrusted with ensuring that the CSR policy is embedded across the company’s operations. The CSR Department assists in implementation and monitoring of the CSR projects, under the hands-on supervision of Ms. Ashima Bhat, Group Head – CSR; and Ms. Nusrat Pathan, Head – CSR.
Read our full interview with Ms. Ashima Bhat here.
2.3 Implementation of CSR Projects
Ground zero implementation of CSR projects requires the involvement of bank employees and departments in branches across India. The HDFC Bank CSR Department works with more than 80 implementing agencies like NGOs, Trusts, Societies, and also collaborates with other corporates. Some of the partners include NGO FUEL, Aga Khan Rural Support Programme and Aroh Foundation. Implementation partners (with no less than 3 years of experience) undergo strict screening based on the company’s internal screening criteria to ascertain their ability to execute CSR projects.
The CSR Department has the responsibility of monitoring approved projects and funds disbursals for such projects. Monitoring mechanisms include visits, meetings and progress/status reporting by the project teams. The Bank’s CSR activities are reviewed by the CSR Committee. Major CSR projects and achievements are highlighted in the Annual Report.
3. CSR Strategy
CSR in HDFC Bank aspires to create significant and sustainable societal value through its social initiatives to embrace the most disadvantaged sections of society, by empowering millions of people to be self-reliant and contribute to India’s growth. The firm has identified SDGs that align best with its material topics.
The bank believes that national development happens when its communities are empowered to attain sustainable livelihood. In this regard, the Bank, under its social umbrella of ‘Parivartan’ is reaching out to communities to make them self-sufficient and empowered. In FY 2018-19, the HDFC Bank Corporate Social Responsibility spending was INR 443.8 crores. It reached out to more than 5.4 crore beneficiaries in the process.
Find out more about Parivartan in this video:
The progress of any country begins when its communities are empowered to attain sustainable means of livelihood. As a step towards progress, HDFC Bank Parivartan is reaching out to communities to help them shift from a vicious cycle of poverty to a pattern of growth and empowerment.
Social impact in 2019

4. Rural Development
I witnessed the firm’s commitment to rural development when I visited two villages in Bihar where the HRDP programme is underway. The CSR team is teaching small farmers organic farming practices, installing solar-powered water pumps, digitising schools and coming up with customised solutions to each neighbourhood’s concerns, which got the whole community proactively involved in the bettering the village.
Holistic Rural Development Programme (HRDP) is the company’s flagship project within Parivartan. It was developed with the belief that Rural Development is central and significant to the nation’s economic development. The rural population is predominantly engaged in agriculture and completely dependent on rainfed irrigation. The programme identifies and addresses the critical needs of each village adopted as part of the programme. There are multiple interventions designed in consultation with the village community and other stakeholders.

These initiatives are in line with the Adarsh Gaon Abhiyan of the Government of India and the UN SDGs. The critical needs of the chosen villages are first identified and addressed in consultation with the village community and other stakeholders. The initiatives are designed on the basis of their needs and openness. All programmes are continuously monitored and assessed for performance and inconsistencies if any, in terms of funds or execution is flagged off.
4.1. HRDP’s various initiatives are in the following areas:
* Improving educational infrastructure
* Promoting quality education
* Healthcare through health camps and awareness sessions
* Construction of individual household sanitation units
* Natural resources management including micro-watershed management, rain water irrigation, soil and water conservation
* Access to water for drinking and irrigation
* Educating people on renewable energy sources like solar, biogas and biomass
* Promoting financial literacy, job-oriented youth training, creating alternate sources of livelihood such as livestock management and entrepreneurship activities like embroidery, knitting, masala making, toy manufacturing etc.
4.2. Parivartan transforms 5 villages in Madhya Pradesh
The Holistic Rural Development Programme (HRDP) was successfully completed in 5 villages in Mandla district of Madhya Pradesh last year. Thanks to this initiative, 824 households now have access to potable water for drinking and farming as well as training in new and improved agriculture practices.
To address community needs in a sustainable and effective manner in all its HRDP projects, HDFC Bank corporate social responsibility team has created long-term solutions in partnership with an NGO and the local community. The beneficiaries of this project included small farmers, youth, landless labourers, children and women.
The project began on 1st September 2015 and has helped transform Ahmadpur, Surajpura, Thonda, Salhedanda and Pondi villages of Mandla district in Madhya Pradesh. More than 3,500 villagers who were mostly dependent on agriculture and associated seasonal labour as their primary source of income, have now found alternate means of sustenance as a result of the programme.
4.3. Drought mitigation in Maharashtra
In November 2018, Govt. of Maharashtra declared some pockets of the state to be drought affected areas. Stepping up to the opportunity, the bank in partnership with an NGO initiated a Drought Mitigation and Awareness Drive to be implemented in chosen project villages as well as adjacent villages. This included a gamut of activities such as vulnerability mapping, awareness creation, water management, preventive measures for water-borne diseases and creating livelihood opportunities.
Water budgeting was done in 65 villages sensitizing more than 11,000 villagers. To enable groundwater recharge, a total of 87 soil and water conservation structures were created. Activities included nallah (drain) widening and deepening, constructing earthen dams, check dams, loose bouldering structures.
To address the acute issue of water scarcity, water storage tanks were arranged at various locations. Moreover, existing hand-pumps water distribution channels were repaired to prevent water wastage through transportation loss and evaporation. Awareness sessions on water purification methods to prevent water borne diseases were also conducted.
Water scarcity leads to migration and issues like family and social disorganization. In order to provide for better job and self-employment opportunities for the youth, the Bank conducted skill development programme in the villages. Through this, more than 120 youth were mobilized and approximately 40 were enrolled for various courses such as hospitality, automobile, welding, masonry, beautician etc.

As part of the Green Ethos Movement’ launched in June 2018, over 48,000 trees were planted through community mobilisation. One of these project villages Anjanpur from Ahmednagar districts is also becoming a model village for afforestation. The Bank partnered with two different NGOs for projects in Jalgaon and Yevatmal districts of Maharashtra. Both the projects were designed to address water issues in areas chronically affected by drought. Interventions under these projects have increased water storage capacities of rivers, dams, wells and ponds.
Moreover, the ground water table level has also increased as a result of bore-well recharge. This has also increased the area under irrigation and cultivation. For our work in these villages, the Bank received the ‘Smart Gram Award’ and the ‘Sant Gadgebaba Gram Swachhata Award’ from the Government of Maharashtra.
5. Skills Training and Livelihood Enhancement
Skill Training and Livelihood Enhancement programme provides training and imparts income generating skills, primarily in agriculture and allied areas such as dairy and poultry. This is focused on people in rural areas, especially young women and youth. This programme aims to skill individuals, helping them to find local jobs thereby curbing migration.
The programme entails:
* Various tailor-made skill and competency building programmes such as job oriented training and placement
* Capacity building and communication skills
* Upskilling for agricultural and allied practices
* Promoting entrepreneurial activities
* Agriculture techniques and livestock management
The nationwide programme has benefited over 1 lakh individuals (excluding those trained under the Sustainable Livelihood Initiative or SLI). As a part of the programme, more than 40,000 youth have received placement- linked skill development training. The company has provided both on-farm training to upskill farmers as well as placement linked training. The Bank’s Training Centre in Bhubaneswar provides training to youth and women in hospitality, tourism, telecom, retail and health care. Over 1900 youth were provided job skilled training and exposure providing them access to approx. 100 companies and institutions in Odisha.
5.1. Sustainable Livelihood Initiative (SLI)
The Sustainable Livelihood Initiative (SLI) is aligned with SDG 6 (Gender Equality and women empowerment). The Bank believes that empowering a single woman can empower an entire family. The Bank guides women from the communities to form Self Help Groups (SHGs) or Joint Liability Groups (JLGs). These groups are then trained on occupational skills, financial literacy, credit counselling and livelihood finance in addition to providing market linkages.

Under SLI, the Bank provides both Financial & Non-Financial services. Financial Products/ Services including Basic Savings Bank Deposit Account (BSBDA) which is a “Zero Balance Account”, Recurring and Fixed Deposits and Insurances are provided to SHG/JLG groups and their members. Non-Financial services include Credit Counselling, and encouraging women to take up entrepreneurship activities.
5.1.a) Case Study: Career Counselling & Skill Training Centre, Bhubaneswar
Due to lack of job-ready skills and career guidance, ambitious and hardworking young individuals like Anjali, Damini, and Saifur could not fulfill their dreams of securing a job and becoming financially independent. Their lives changed when they enrolled at the Career Counselling and Skills Training Centre and acquired the skills to become job-ready, along with 2000 women like them. After successfully completing the three-month Skills Training programme in sectors ranging from telecom, healthcare, retail, tourism & hospitality and BFSI, they have now realized their dream. The youth from Bhubaneswar have been offered employment at leading organizations across the city in their area of specialization.
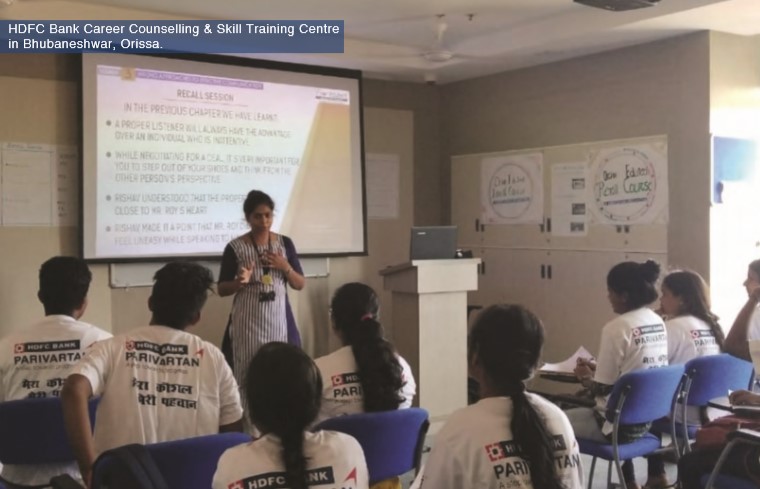

In addition to the skills training, the Bank also provided career counselling to over 8,000 students from schools in and around Bhubaneswar to help them pursue appropriate career opportunities. Besides career counselling, the training sessions comprised of on-campus theory and training, industry visits, meets with industry professionals and on-field internships. Participants were provided with personalized career assessment, career toll-free hotline, career guidance and booklets, SMS alerts, and access to HDFC Parivartan job fairs.
5.1.b) Employment opportunities for 3,000 youth in Nagpur
In FY 2018-19, HDFC launched a Career Counselling and Skills Training Centre for youth in Nagpur, to train them on skills necessary to be job ready. Young women from over 180 villages in and around Nagpur joined the first batch of students at the training centre. On successful completion of the nine-month course, they received certificates from the National Skills Development Corporation (NSDC), making them eligible for jobs in Retail, Telecom, and Tourism & Hospitality.
In addition to the skills training, the Bank has also provided career counselling to over 13,000 students across 65 schools in and around Nagpur to help them pursue appropriate career opportunities. The youth were not only counselled on career opportunities but also given personalized career assessment, career toll-free hotline, career guidance booklet, HDFC Parivartan scholarship booklet and access to job fairs. This programme helps the Bank contribute to SDG 1 – No Poverty and SDG 8 – Decent Work and Economic Growth.
6. Education
Education is the key for developing the economy and transforming an individual’s life. Hence, Parivartan puts focus on inclusive and quality education for all. The Bank strives to promote a conducive learning environment in schools. The Bank’s efforts in the area of education include teacher training, HDFC Bank CSR Parivartan scholarships and career guidance. It also includes provision of infrastructure support, such as building toilets in schools and improving classrooms.

Teacher training provides teachers with alternative teaching pedagogy, improves their soft skills and promotes innovation. The programmes also focus on providing quality education through remedial classes, learning camps, special scholarships etc. This programme is in line with the Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan of the Government of India and SDG 4 (Promoting Quality Education). Navachar Pustika (Innovations Handbook), is a compilation of innovative teaching ideas contributed by teachers themselves. These zero cost, high impact ideas are part of HDFC Bank’s ‘Teaching-the-Teacher’ (3T) programme under #Parivartan. The 3T programme is run in partnership with Sri Aurobindo Society.


