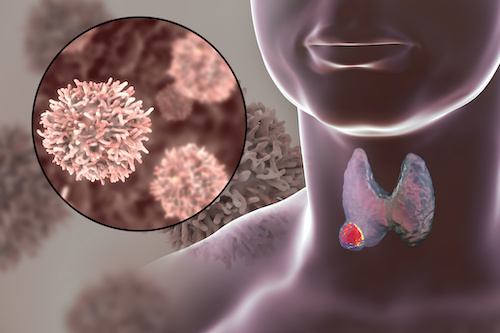
What Is Thyroid Cancer? Factors You Didn’t Know Could Increase Risk
Related Articles
Delhi: नेहरू प्लेस में हाईटेक मल्टी लेवल पार्किंग का उद्घाटन, जानें खासियत
दिल्ली के नेहरू प्लेस में आज से पार्किंग की समस्या का सामाधान हो गया है। उपराज्यपाल विनय कुमार सक्सेना की उपस्थिति में, मुख्यमंत्री रेखा...
Ananya Birla’s Birla Studios Engages Prominent Filmmakers for Upcoming Projects
Entrepreneur Ananya Birla has formally entered the world of film production with the launch of Birla Studios, a new production house poised to make...
Bus Conductor in Bengaluru Goes Viral for Reading Books During Breaks, exemplifying dedication to education amid her busy job.
A female bus conductor in Bengaluru has garnered attention for her dedication to both her job and pursuing education simultaneously. During a break in...