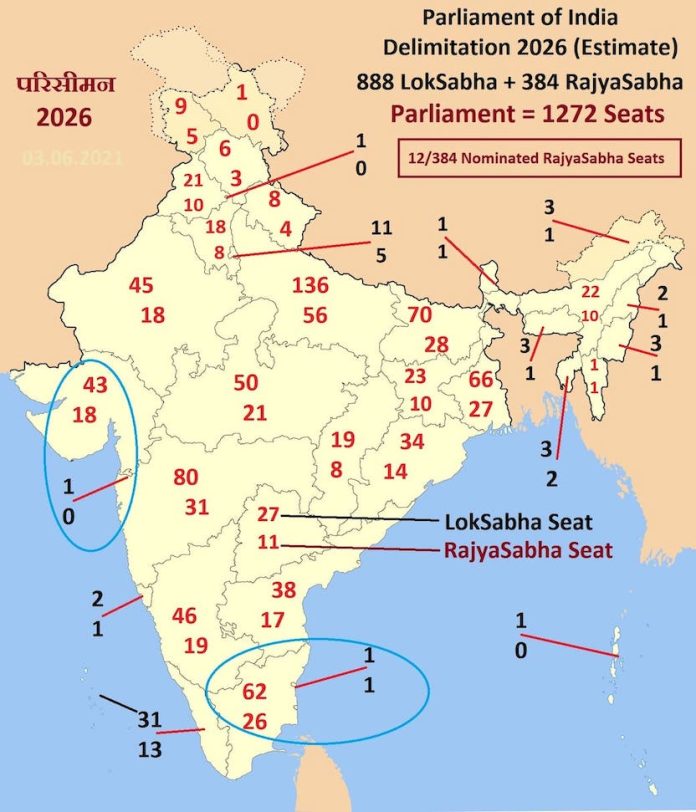
Trump-Zelensky विवाद पर बाकी देशों का रवैया
यूरोपीय नेताओं ने Trump के साथ विवादित बैठक के बाद Ukrain और राष्ट्रपति Volodymyr Zelensky के प्रति अपना समर्थन जाहिर किया है। France,Sweden और Estonia के नेताओं ने Russia की आक्रामकता की निंदा करते हुए Ukrain की सुरक्षा और शांति की जरूरतों पर जोर दिया। यूरोपीय संघ और विभिन्न यूरोपीय देशों ने यूक्रेन के संघर्ष में अपना समर्थन जताया। अमेरिकी राष्ट्रपति डोनाल्ड ट्रंप और यूक्रेनी प्रेसिडेंट जेलेंस्की के बीच तीखी बहस के बाद Europe लगभग खुलकर यूक्रेन के समर्थन में आ गया है। French President Emmanuel Macron, Sweden के PM Ulf Kristersson और एस्टोनिया के विदेश मंत्री मार्गस त्साहक्ना ने सबसे अहम बयानों में रूस के खिलाफ अपना रुख स्पष्ट किया। उन्होंने इस बात पर जोर दिया कि शांति की राह में सिर्फ पुतिन की आक्रमण की नीति है जो रोड़ा बन रही है।
Estonia Foreign Minister, Margus Tsahkna ने दिया Ukrain को समर्थन
एस्टोनिया के Foreign Minister, Margus Tsahkna ने यूक्रेन के समर्थन की प्रतिबद्धता जताई और कहा कि यूरोप के पास पर्याप्त संसाधन हैं जो यूक्रेन की सहायता कर सकते हैं। स्पेन, लात्विया, लिथुआनिया, जर्मनी और पोलैंड ने भी यूक्रेन के समर्थन में अपने बयान जारी किए। यूक्रेन के राष्ट्रपति कार्यालय के प्रमुख ने सुरक्षा की जरूरतों को समझाते हुए कहा कि बिना वास्तविक सुरक्षा गारंटी के युद्ध फिर से लौट सकता है.
फ्रांस के राष्ट्रपति Emmanuel Macron ने कहा,”Ukrain पीड़ित है। हमने तीन साल पहले यूक्रेन की मदद करके और रूस पर प्रतिबंध लगाकर सही किया था।” हम से उनका मतलब अमेरिकी यूरोपीय, कनाडाई, जापानी और कई अन्य से है, जिन्होंने एकमत से Russia पर प्रतिबंध लगाया था।